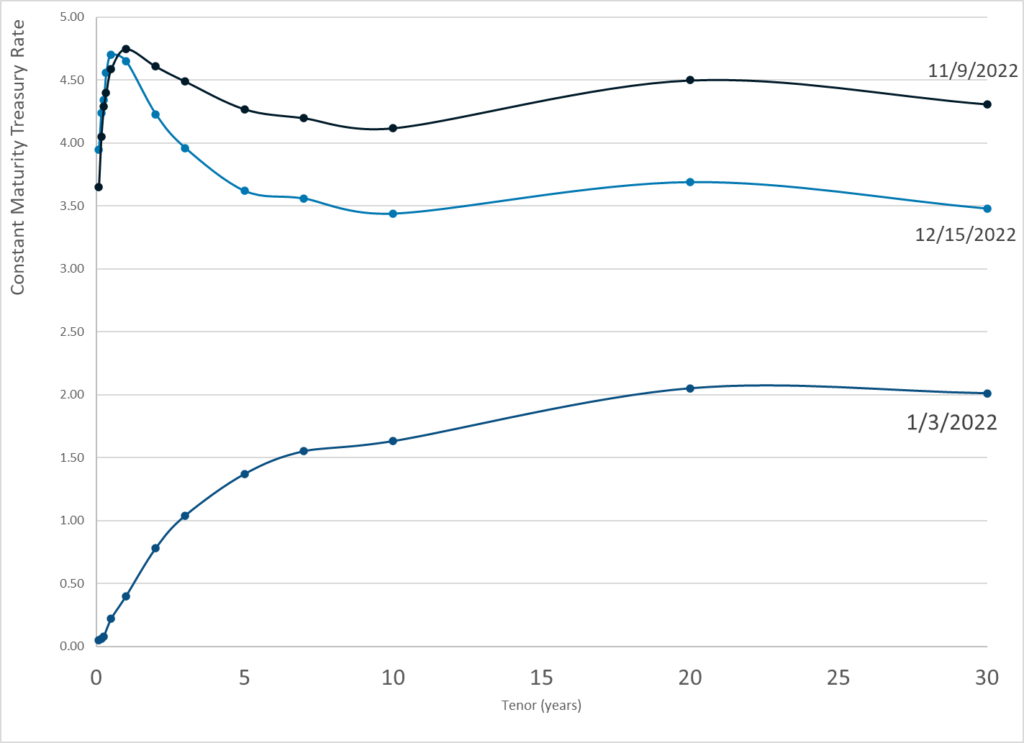
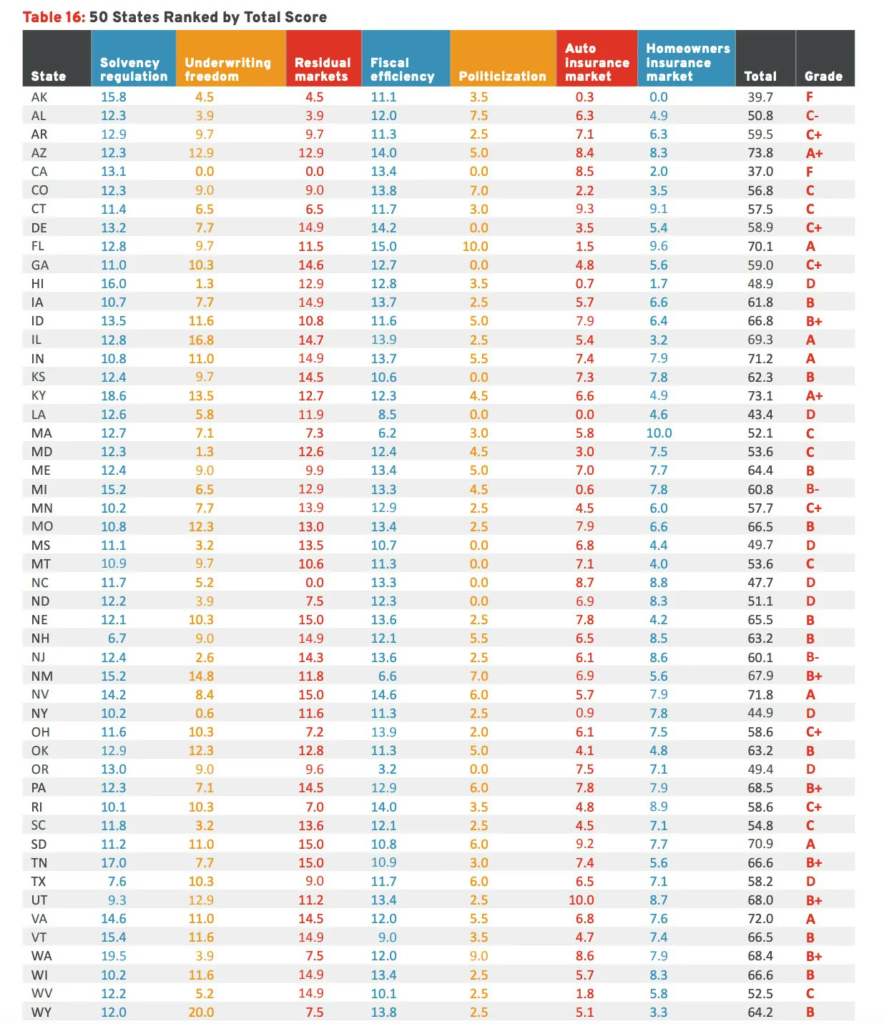
Link: https://khn.org/news/article/coroners-medical-examiners-doctor-or-not-death-investigations/
Excerpt:
When a group of physicians gathered in Washington state for an annual meeting, one made a startling revelation: If you ever want to know when, how — and where — to kill someone, I can tell you, and you’ll get away with it. No problem.
That’s because the expertise and availability of coroners, who determine cause of death in criminal and unexplained cases, vary widely across Washington, as they do in many other parts of the country.
….
Each state has its own laws governing the investigation of violent and unexplained deaths, and most delegate the task to cities, counties, and regional districts. The job can be held by an elected coroner as young as 18 or a highly trained physician appointed as medical examiner. Some death investigators work for elected sheriffs who try to avoid controversy or owe political favors. Others own funeral homes and direct bodies to their private businesses.
Overall, it’s a disjointed and chronically underfunded system — with more than 2,000 offices across the country that determine the cause of death in about 600,000 cases a year.
…..
Belcher’s crusade succeeded in changing some aspects of Washington’s coroner system when state lawmakers approved a new law last year, but efforts to reform death investigations in California, Georgia, and Illinois have recently failed.
Rulings on causes of death are often not cut-and-dried and can be controversial, especially in police-involved deaths such as the 2020 killing of George Floyd. In that case, Minnesota’s Hennepin County medical examiner ruled Floyd’s death a homicide but indicated a heart condition and the presence of fentanyl in his system may have been factors. Pathologists hired by Floyd’s family said he died from lack of oxygen when a police officer kneeled on his neck and back.
….
In 2009, the National Research Council recommended that states replace coroners with medical examiners, describing a system “in need of significant improvement.”
Massachusetts was the first state to replace coroners with medical examiners statewide in 1877. As of 2019, 22 states and the District of Columbia had only medical examiners, 14 states had only coroners, and 14 had a mix, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Author(s): Samantha Young
Publication Date: 20 Dec 2022
Publication Site: Kaiser Health News