Graphic:
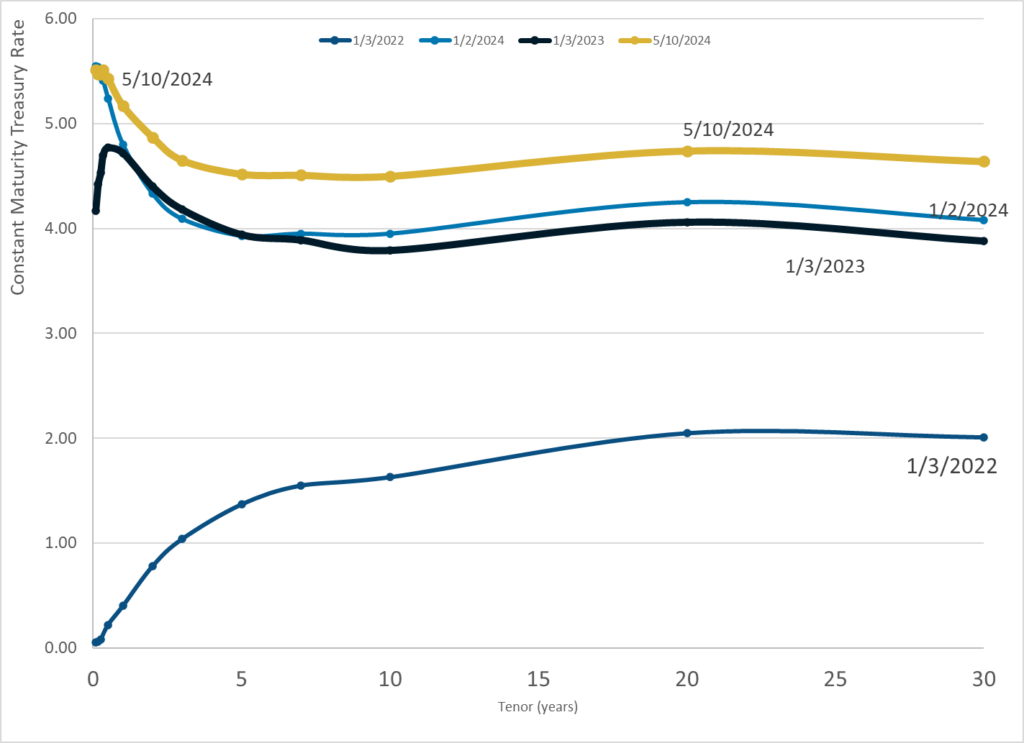
Publication Date: 10 May 2024
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
All about risk
Graphic:

Publication Date: 10 May 2024
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Graphic:
Publication Date: 6 May 2024
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Graphic:
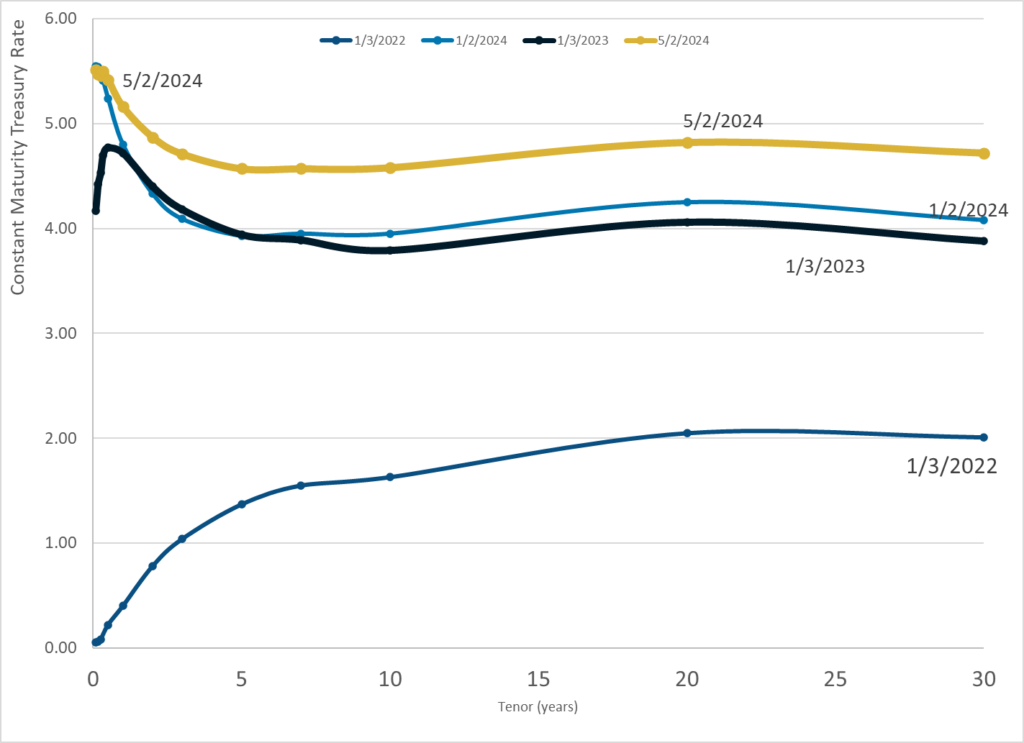
Publication Date: 2 May 2024
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Graphic:
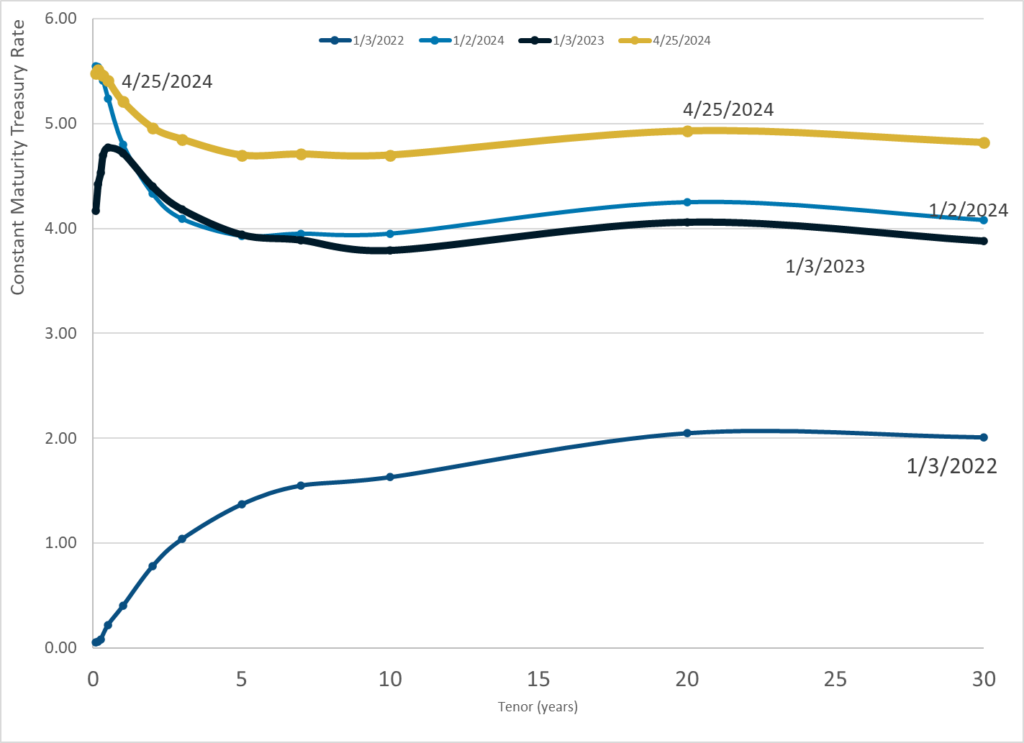
Publication Date: 25 Apr 2024
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Graphic:
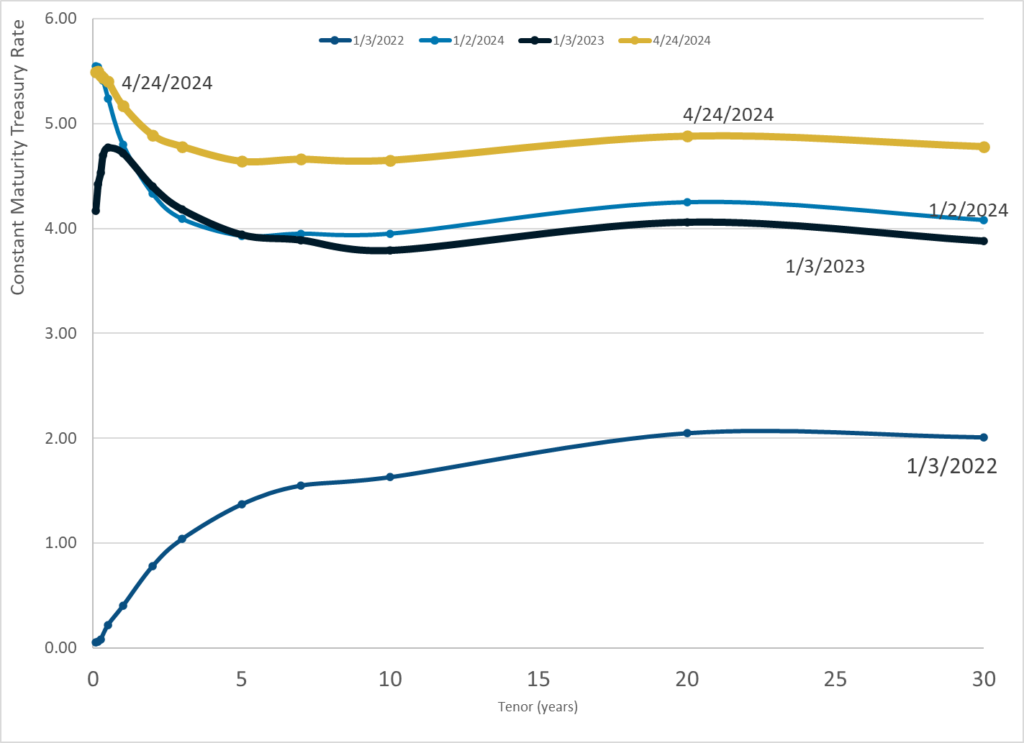
Publication Date: 24 Apr 2024
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Graphic:
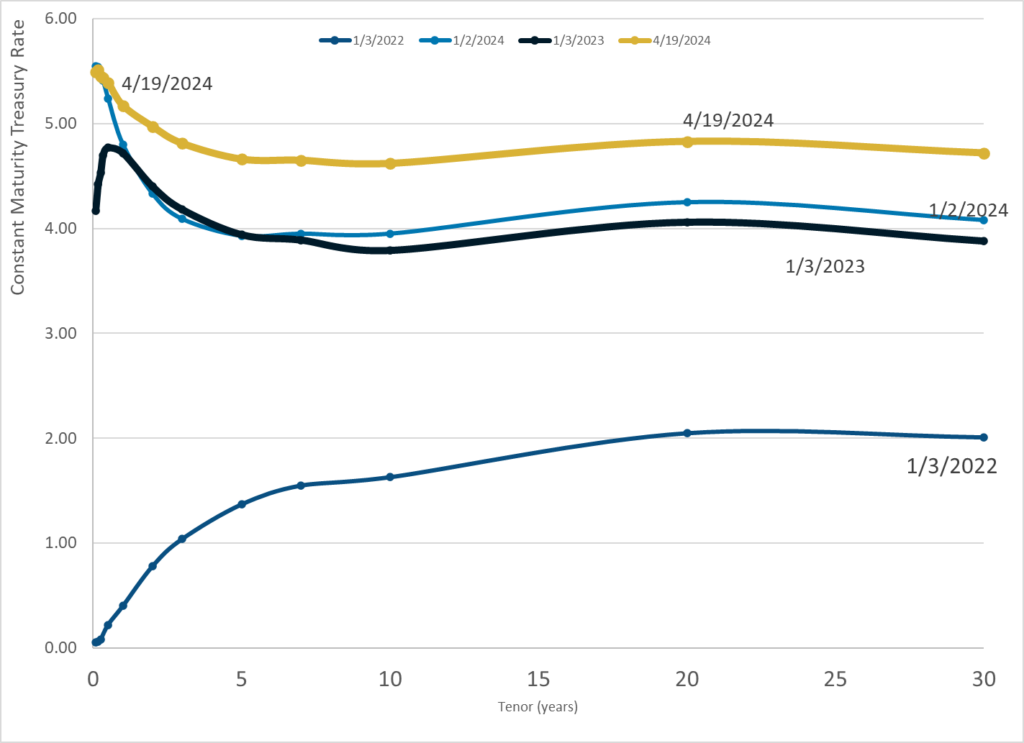
Publication Date: 19 Apr 2024
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Graphic:
Publication Date: 5 Apr 2024
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Graphic:
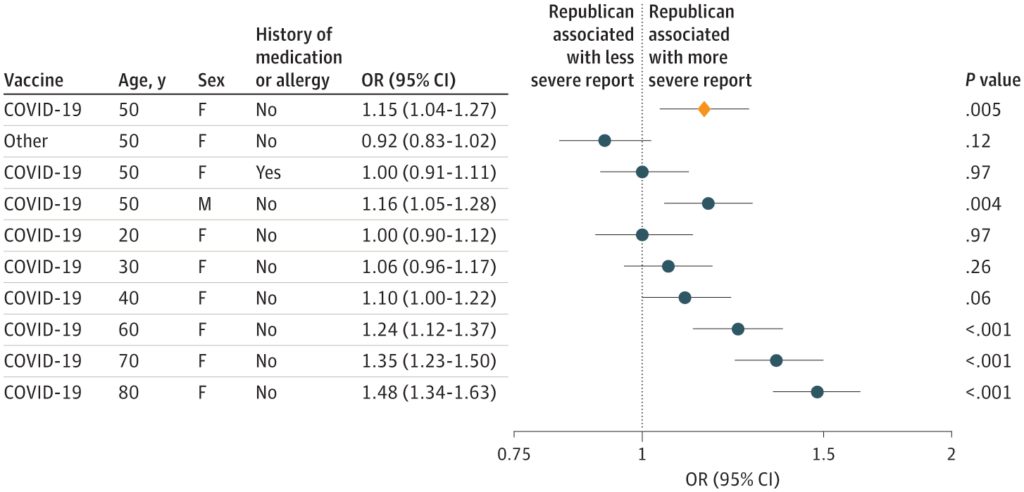
Abstract:
Importance Antivaccine sentiment is increasingly associated with conservative political positions. Republican-inclined states exhibit lower COVID-19 vaccination rates, but the association between political inclination and reported vaccine adverse events (AEs) is unexplored.
Objective To assess whether there is an association between state political inclination and the reporting rates of COVID-19 vaccine AEs.
Design, Setting, and Participants This cross-sectional study used the AE reports after COVID-19 vaccination from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) database from 2020 to 2022, with reports after influenza vaccines from 2019 to 2022 used as a reference. These reports were examined against state-level percentage of Republican votes in the 2020 US presidential election.
Exposure State-level percentage of Republican votes in the 2020 US presidential election.
Main Outcomes and Measures Rates of any AE among COVID-19 vaccine recipients, rates of any severe AE among vaccine recipients, and the proportion of AEs reported as severe.
Results A total of 620 456 AE reports (mean [SD] age of vaccine recipients, 51.8 [17.6] years; 435 797 reports from women [70.2%]; a vaccine recipient could potentially file more than 1 report, so reports are not necessarily from unique individuals) for COVID-19 vaccination were identified from the VAERS database. Significant associations between state political inclination and state AE reporting were observed for all 3 outcomes: a 10% increase in Republican voting was associated with increased odds of AE reports (odds ratio [OR], 1.05; 95% CI, 1.05-1.05; P < .001), severe AE reports (OR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.24-1.26; P < .001), and the proportion of AEs reported as severe (OR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.20-1.22; P < .001). These associations were seen across all age strata in stratified analyses and were more pronounced among older subpopulations.
Conclusions and Relevance This cross-sectional study found that the more states were inclined to vote Republican, the more likely their vaccine recipients or their clinicians reported COVID-19 vaccine AEs. These results suggest that either the perception of vaccine AEs or the motivation to report them was associated with political inclination.
Author(s):David A. Asch, MD, MBA1,2; Chongliang Luo, PhD3; Yong Chen, PhD2,4,5Author(s):
Publication Date: 29 Mar 2024
Publication Site: JAMA Network Open
Link:https://mishtalk.com/economics/ominous-technical-trends-for-us-treasury-bulls-three-durations/
Graphic:

Excerpt:
Technical patterns on 2-year, 10-year, and 30-year US treasuries all suggest yields are heading higher. Let’s also discuss the supporting fundamental case.
Centerpoint explains “An ascending triangle chart pattern is a bullish technical pattern that typically signals the continuation of an uptrend. They can signal a coming bullish breakout above an area of resistance after it has been tested several times.”
Many people do not believe in technical patterns, others believe in nothing else. Certainly, technical patterns fail often enough.
My take is they work best as entry and exit point strategies, especially when fundamentals align.
Author(s): Mike Shedlock
Publication Date: 3 Apr 2024
Publication Site: MishTalk
Graphic:
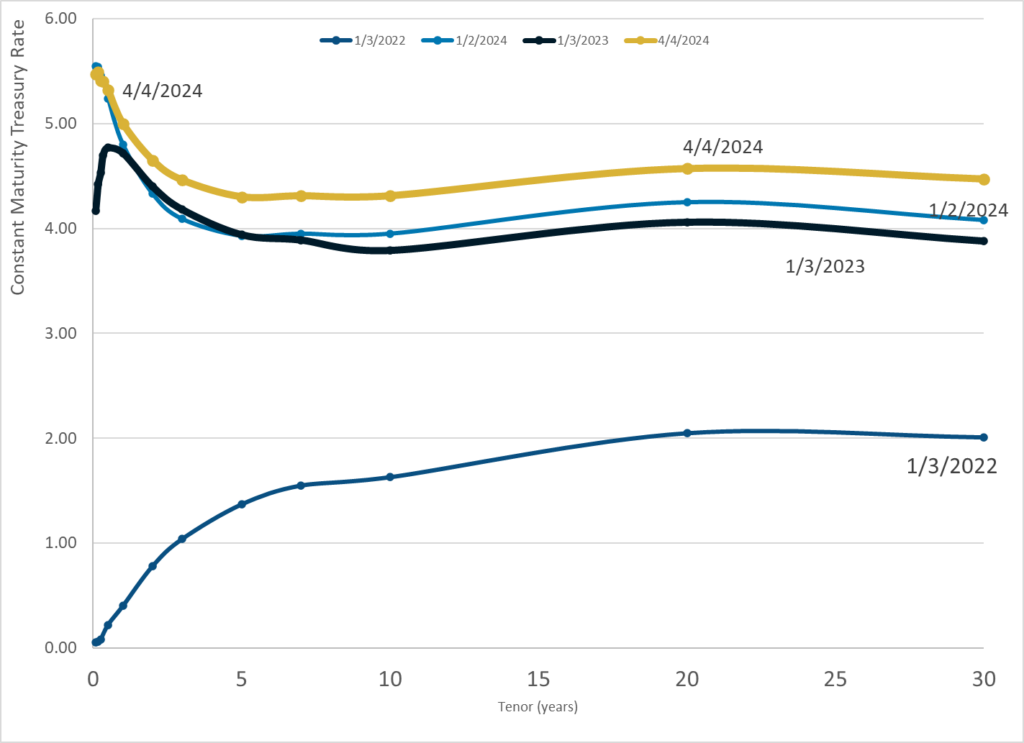
Publication Date: 4 Apr 2024
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Graphic:
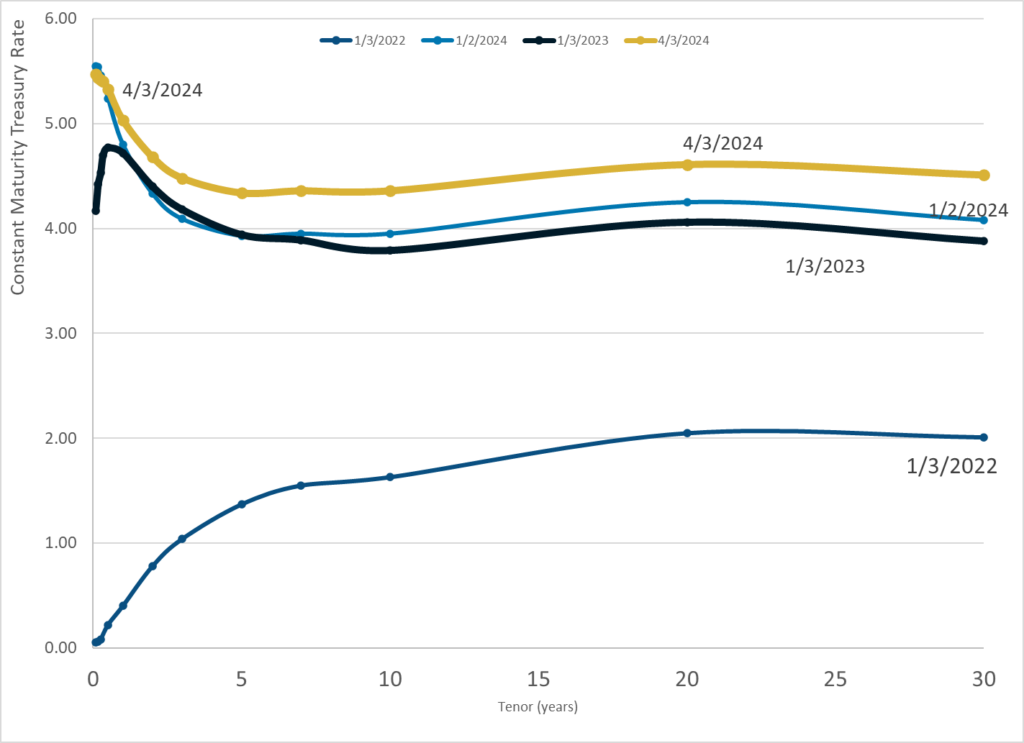
Publication Date: 3 Apr 2024
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Graphic:
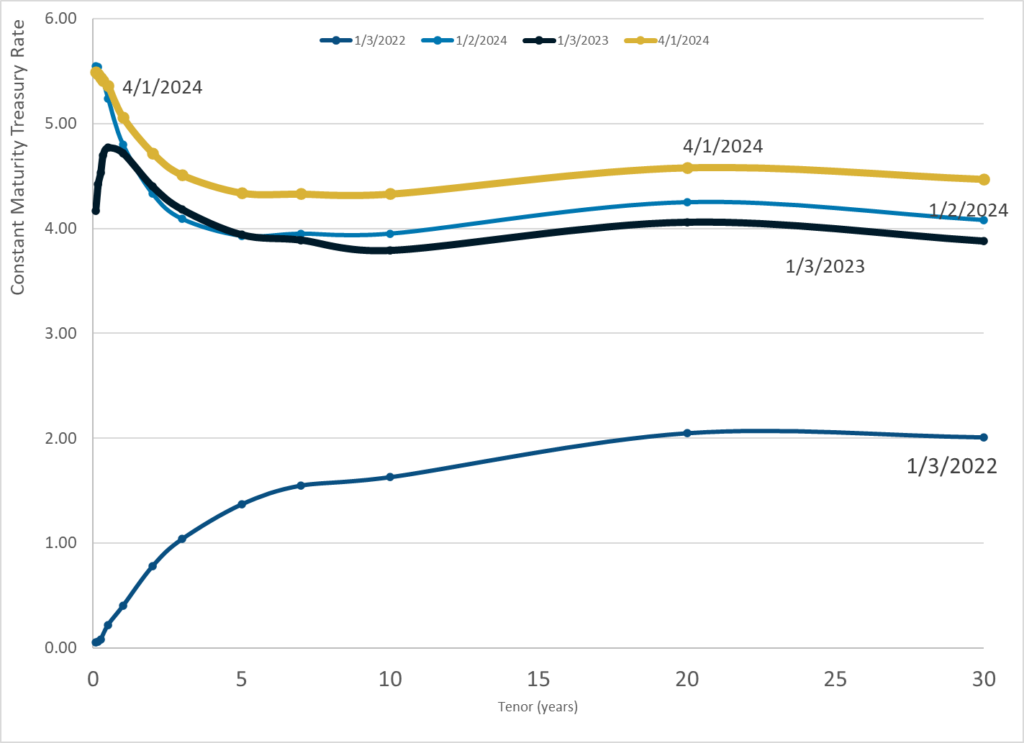
Publication Date: 1 Apr 2024
Publication Site: Treasury Dept