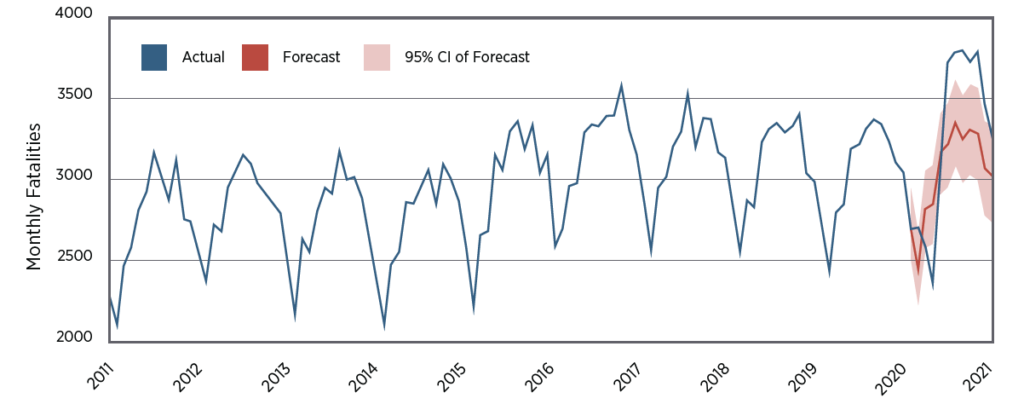
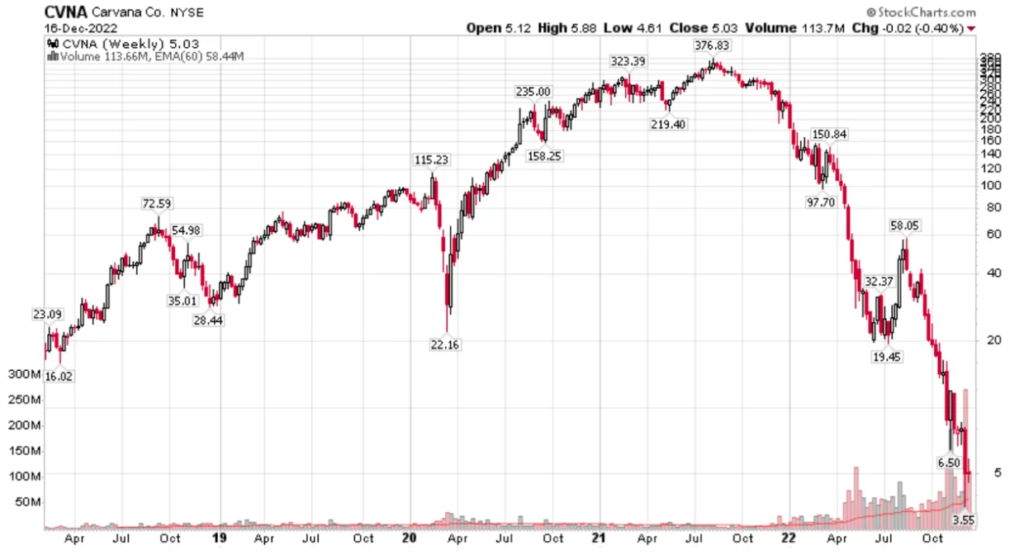
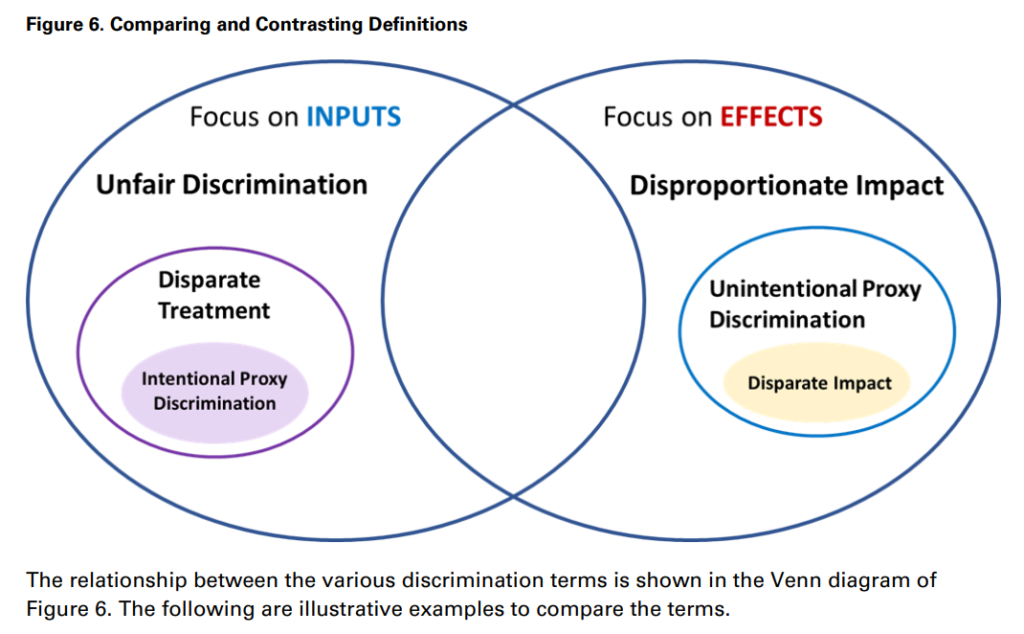
Link:https://danluu.com/nothing-works/
Excerpt:
It’s also true at the firm level that it often takes an unusually unreasonable firm to produce a really great product instead of just one that’s marketed as great, e.g., Volvo, the one car manufacturer that seemed to try to produce a level of structural safety beyond what could be demonstrated by IIHS tests fared so poorly as a business that it’s been forced to move upmarket and became a niche, luxury, automaker since safety isn’t something consumers are really interested in despite car accidents being a leading cause of death and a significant source of life expectancy loss. And it’s not clear that Volvo will be able to persist in being an unreasonable firm since they weren’t able to survive as an independent automaker. When Ford acquired Volvo, Ford started moving Volvos to the shared Ford C1 platform, which didn’t fare particularly well in crash tests. Since Geely has acquired Volvo, it’s too early to tell for sure if they’ll maintain Volvo’s commitment to designing for real-world crash data and not just crash data that gets reported in benchmarks. If Geely declines to continue Volvo’s commitment to structural safety, it may not be possible to buy a modern car that’s designed to be safe.
Most markets are like this, except that there was never an unreasonable firm like Volvo in the first place. On unreasonable employees, Yossi says
Who can, and sometimes does, un-rot the fish from the bottom? An insane employee. Someone who finds the forks, crashes, etc. a personal offence, and will repeatedly risk annoying management by fighting to stop these things. Especially someone who spends their own political capital, hard earned doing things management truly values, on doing work they don’t truly value – such a person can keep fighting for a long time. Some people manage to make a career out of it by persisting until management truly changes their mind and rewards them. Whatever the odds of that, the average person cannot comprehend the motivation of someone attempting such a feat.
It’s rare that people are willing to expend a significant amount of personal capital to do the right thing, whatever that means to someone, but it’s even rarer that the leadership of a firm will make that choice and spend down the firm’s capital to do the right thing.
Economists have a term for cases where information asymmetry means that buyers can’t tell the difference between good products and “lemons”, “a market for lemons”, like the car market (where the term lemons comes from), or both sides of the hiring market. In economic discourse, there’s a debate over whether cars are a market for lemons at all for a variety of reasons (lemon laws, which allow people to return bad cars, don’t appear to have changed how the market operates, very few modern cars are lemons when that’s defined as a vehicle with serious reliability problems, etc.). But looking at whether or not people occasionally buy a defective car is missing the forest for the trees. There’s maybe one car manufacturer that really seriously tries to make a structurally safe car beyond what standards bodies test (and word on the street is that they skimp on the increasingly important software testing side of things) because consumers can’t tell the difference between a more or less safe car beyond the level a few standards bodies test to. That’s a market for lemons, as is nearly every other consumer and B2B market.
Author(s): Dan Luu
Publication Date: March 2022, accessed 7 Jun 2023
Publication Site: Dan Luu