Graphic:
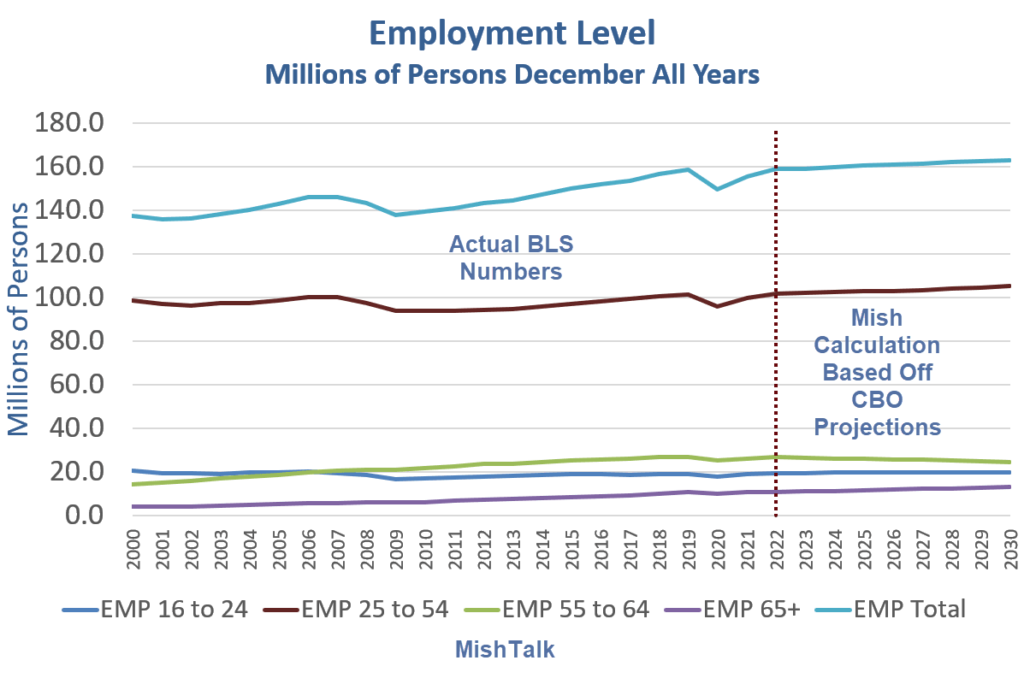
Excerpt:
If you work one hour, you are employed. If you don’t have a job and fail to look for one, you are not considered unemployed, rather, you drop out of the labor force.
Looking for job openings on Jooble or Monster or in the want ads does not count as “looking for a job”. You need an actual interview or send out a resume.
These distortions artificially lower the unemployment rate, artificially boost full-time employment, and artificially increase the payroll jobs report every month.
Q&A What’s Going On?
Q: Hey Mish, What’s Going On?
A: People are taking on second part time jobs to make ends meet. But full time employment is stagnant no matter how one slices and dices the revisions.
Author(s): Mike Shedlock
Publication Date: 3 Feb 2023
Publication Site: Mish Talk