Link: https://oig.hhs.gov/documents/evaluation/9808/OEI-02-20-00492.pdf
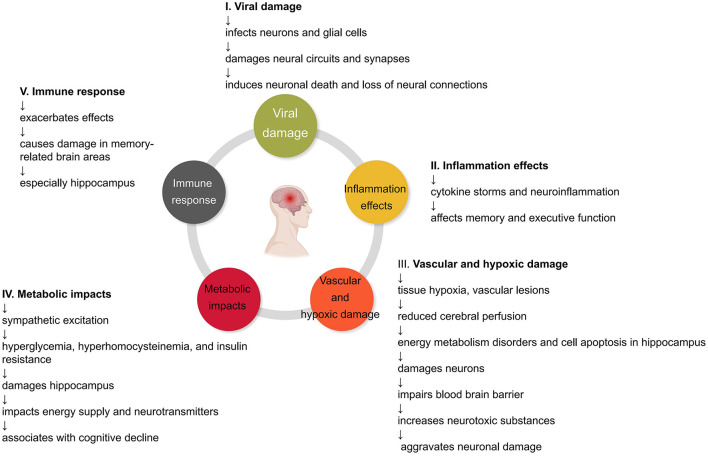
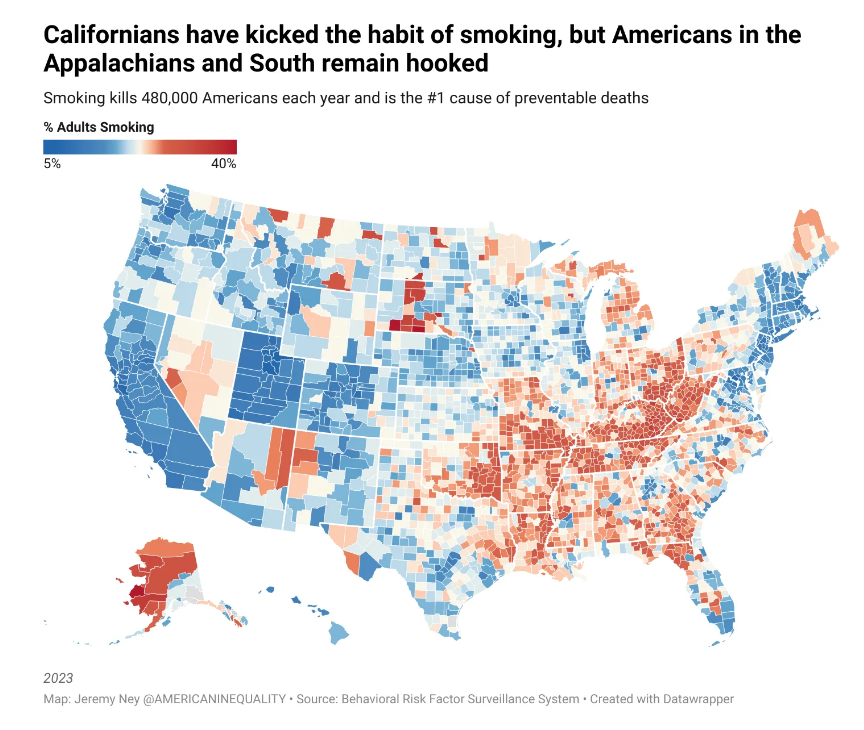
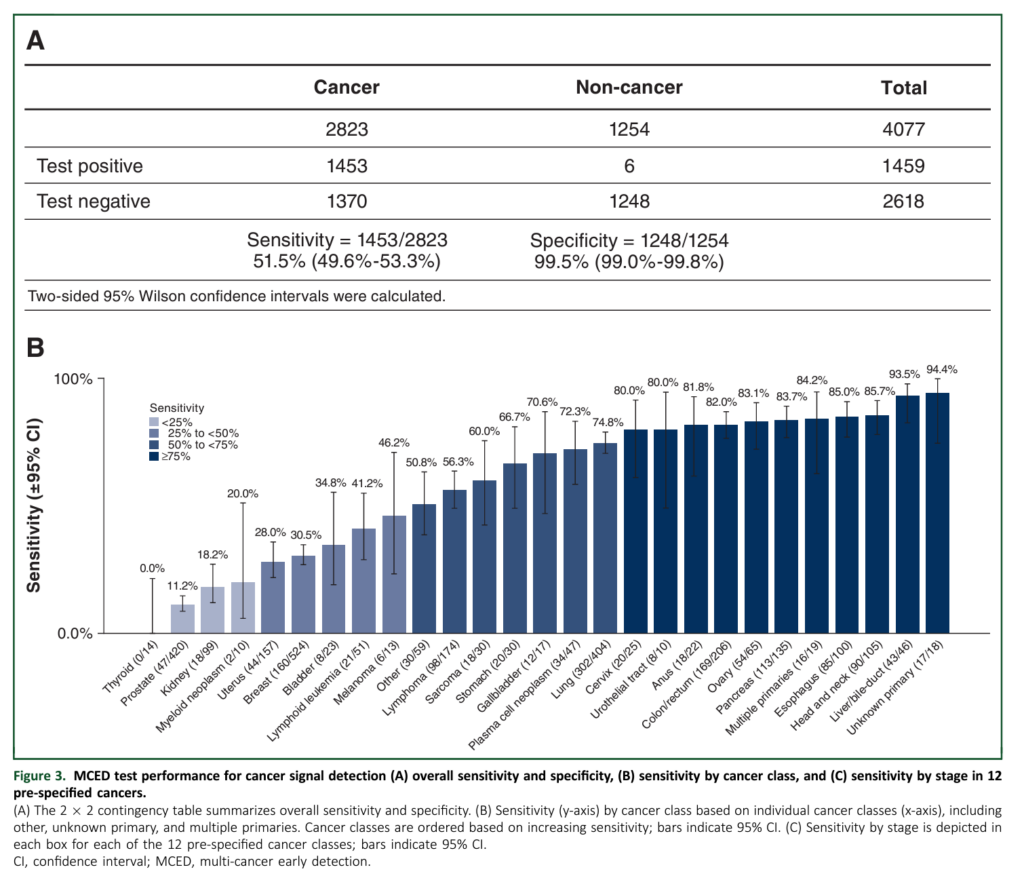
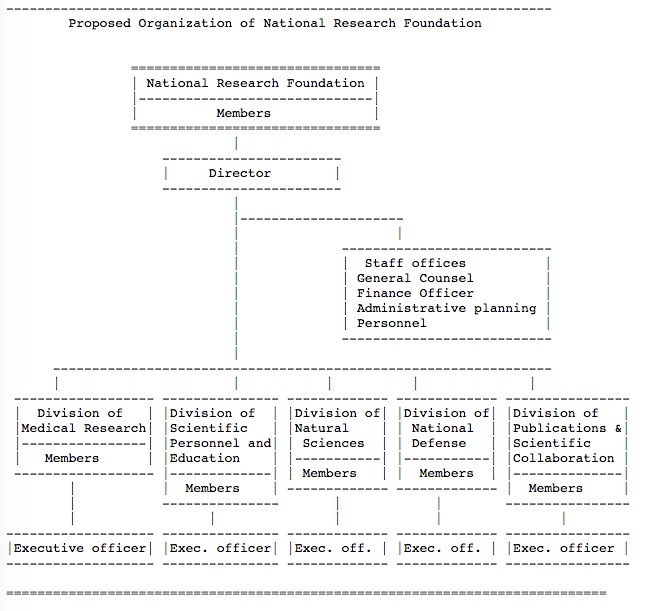
Graphic:

Excerpt:
OIG recommends that the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS):
1. Implement and expand upon its policies and programs to strengthen the nursing home workforce.
2. Reassess nurse aide training and certification requirements.
3. Update the nursing home requirements for infection control to incorporate lessons learned from the pandemic.
4. Provide effective guidance and assistance to nursing homes on how to comply with updated infection control requirements.
5. Facilitate sharing of strategies and information to help nursing homes overcome challenges and improve care.
CMS did not explicitly state its concurrence or nonconcurrence for the five recommendations.
Author: Christi A. Grimm
Publication Date: February 2024
Publication Site: Office of the Inspector General, HHS