Link: https://www.nirsonline.org/reports/greatrecession/
Webinar slides: https://www.nirsonline.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/FINAL-Great-Recession-Retro-Public-Webinar.pdf
Video:
Graphic:
Excerpt:
This report finds that state and local government retirement systems on the whole successfully navigated the 2007 to 2009 Global Financial Crisis. Moreover, public retirement systems across the nation have adapted in the years since the recession by taking actions to ensure continued long-term resiliency.
Examining the Experiences of Public Pension Plans Since the Great Recession is authored by Tyler Bond, NIRS Research Manager, Dan Doonan, NIRS Executive Director, Todd Tauzer, Segal Vice President and Actuary, and Ronald Temple, Lazard Managing Director and Co-Head of Multi-Asset and Head of U.S. Equity.
The report finds:
- The majority of public pension plans recovered their pre- recession asset levels within six years, while continuing to pay over a trillion dollars in benefits. In recent years, public plans have reported record-high asset levels.
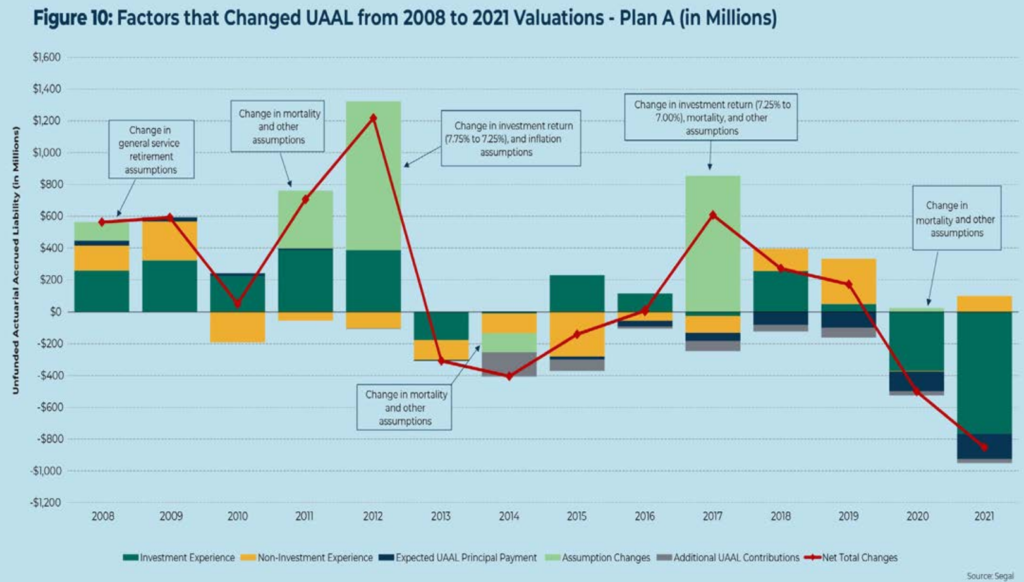
- Discount rates, or the assumed rate of return on investments, have broadly decreased from eight to seven percent for the median public pension plan, based on actuarial and financial forecasts of future market returns.
- Generational mortality tables, possible today with more advanced financial modeling software, have been broadly adopted by nearly all large public plans and future longevity improvements are now incorporated into standard financial projections.
- Many public plans have shortened amortization periods, or the period of time required to pay off an unfunded actuarial accrued liability, to align with evolving actuarial best practices. Tightening amortization periods, akin to paying off a mortgage more quickly, has had the effect of increasing short- term costs. In the long run, plans and stakeholders will benefit.
- The intense focus on public plan investment programs since the Great Recession misses the more important structural changes that generally have had a larger impact on plan finances and the resources necessary for retirement security.
- Plans have adjusted strategic asset allocations in response to market conditions. With less exposure to public equities and fixed income, plans increased exposure to real estate, private equity, and hedge funds.
- Professionally managed public defined benefit plans rebalance investments during volatile times and avoid the behavioral drag observed in retail investment.
Author(s): Dan Doonan, Ron Temple, Todd Tauzer, Tyler Bond
Publication Date: October 2022
Publication Site: NIRS