Graphic:
Excerpt:
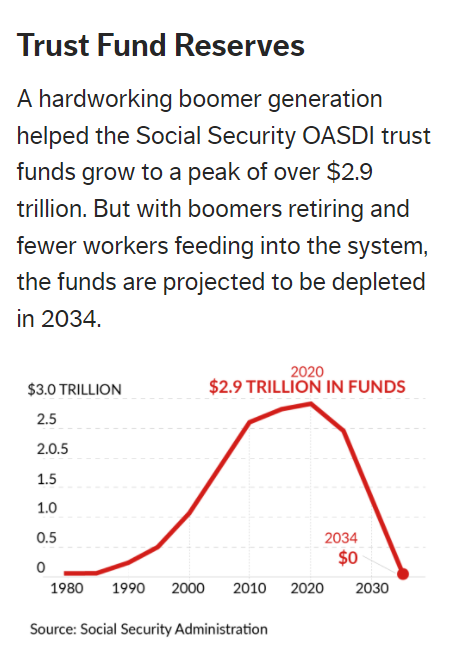
How did we get here? As long predicted, demographics explain a good deal: In a decade, the entirety of the boomer generation — some 70 million Americans born between 1946 and 1964 — will have hit retirement age. As a result, the number of people receiving Social Security benefits come 2034 will be more than double the beneficiaries in 1985.
But what wasn’t known as accurately was how much longer those boomers would live. “From 1940 to 2019, life expectancies at age 65 have increased by about 6.5 years,” says Amy Kemp, chair of the Social Security Committee of the American Academy of Actuaries.
The impact: Many workers will be receiving benefits for a longer period of time. And those with higher incomes, which are generally those who receive higher benefit amounts, tend to live longer on average.
Author(s): John Waggoner
Publication Date: 1 March 2022
Publication Site: AARP