Link: https://govmoneynews.com/bills-blog/f/is-ed-kanes-gathering-crisis-still-gathering-steam
Excerpt:
Back in 1985, Ed Kane penned a prophetic volume identifying a blooming mess in financial markets. His book, The Gathering Crisis in Federal Deposit Insurance, reliably warned of taxpayer exposure to losses ultimately unleashed in the savings and loan crisis.
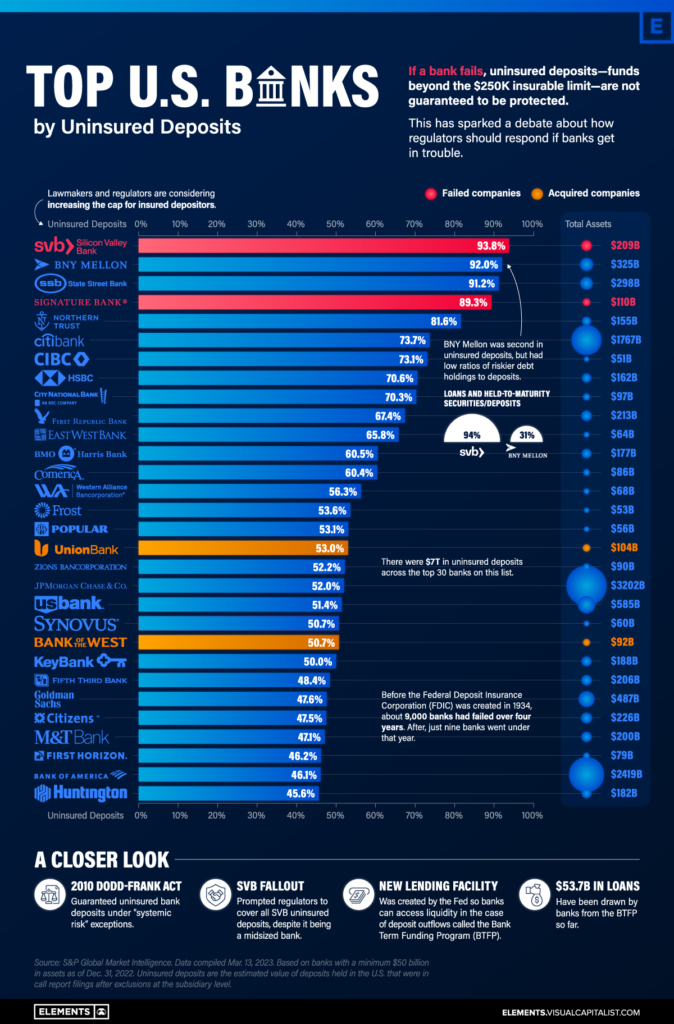
Cycles of ensuing regulatory reforms, crises and scandals have only reinforced the timeliness of the lessons that Kane offered us decades ago. Those lessons became particularly poignant in light of the failure of Silicon Valley Bank and several other large banks earlier this year.
Kane’s 1980s warnings remain worthy of scrutiny and reflection, and underscore questions whether industry and regulatory reforms have simply left us on the edge of another precipice. The financial conditions of the FDIC and the Federal Reserve – and their implications for the U.S. Treasury and American taxpayers – deserve close scrutiny, as well as recommendations for fundamental reform.
….
“In an economic environment in which deposit institutions are highly levered and entering new businesses every day and in which interest rates are highly volatile, systematically mispricing deposit insurance guarantees encourages deposit institution managers to position their firms on the edge of financial disaster. Metaphorically, deposit-insurance authorities are paying deposit-institution managers to overload the deposit-insurance jalopy, to drive it too fast, and even to break dance on its hood as it careens through interest rate mountains and over back-country roads. Reformers’ ultimate goals must be to confront institutions whose risk-taking imposes socially unacceptable risks on its federal guarantors with a combination of reduced coverages and increased fees sufficient to move them to adopt safer modes of operation.” (p. 147)
“Of course, just how safe, reliable, and comfortable a ride the nation enjoys depends also on the macroeconomic policies that the government follows. If Congress could bring government spending under long-run control, monetary policy would not have to push interest rates over so wide a cycle. Reducing the volatility of interest rates would relieve the car’s drivers of the need to take it over quite so dangerous a set of roads.” (p. 165)
Author(s): Bill Bergman
Publication Date: 20 Dec 2023
Publication Site: Bill’s Blog at GovMoneyNews