Excerpt:
Right now, men in the United States, whether infants or elders, are more likely to die at younger ages than their female counterparts. Male life expectancy at birth is currently 75.8 years — 5.3 years less than it is for women. The gap between American men and women had mostly been narrowing gradually for the first decade of this century, then holding relatively steady, until the Covid-19 pandemic, when it widened sharply to 5.8 years, the largest difference since 1996. While living longer doesn’t guarantee that those extra years are healthy or meaningful, life expectancy remains a rough proxy for overall health.
Over the past several years, men have died at higher rates than women from 14 of the top 15 causes of death. The only exception has been Alzheimer’s disease — and that, at least to some extent, is because more women live long enough to develop it. Young men in particular are heavily affected by deaths of despair, like suicides and overdoses, which significantly lower overall male life expectancy. Native American and Black men have the shortest lives; across all racial groups, men die younger than women.
That disparity has many causes, one of which is that men simply don’t go to the doctor as often. The problem begins early: After pediatric care, young men largely disappear from medical settings until after serious issues arise. Women tend to see their gynecologists regularly; men have no clear equivalent. The Affordable Care Act covers only one preventive service specifically targeting men, while it lists 27 for women (some of which are related to pregnancy). HPV vaccination, for example, recommended for all adolescents, still feels mostly associated with girls, when HPV-related throat cancers are now more common in men than cervical cancers are in women.
….
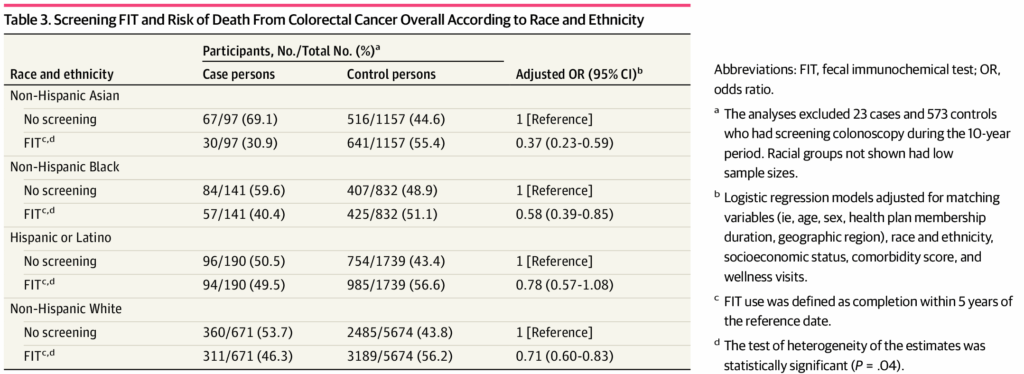
By the time the man came into the E.R. where I work, the cancer had already spread throughout his body. He knew that colon cancer ran in his family, yet he didn’t get his first colonoscopy until almost a decade past the recommended time — until he decided he could no longer ignore the blood he had been seeing in his stool for a year. Work occupied his mind; besides, nothing really felt like something he couldn’t push through. After his diagnosis, surgery and chemotherapy temporarily suppressed the disease. He felt better, so he stopped seeing his doctors.
….
Around the world, in countries where precarious manhood is felt more strongly, men tend to have higher rates of risky health behaviors and lower life expectancy. Where these beliefs are strongest among the 60-plus countries surveyed, male life expectancy is about 6.7 years shorter than in countries where they are weakest — even after controlling for wealth, gender equality and number of physicians. The United States ranks higher in precarious manhood beliefs than its peers like Spain, Germany and Finland; correspondingly, American men die younger. In a forthcoming paper, researchers including Bosson and Vandello found that the more strongly a country endorses precarious manhood, the more likely its men are to die from high-risk causes — drownings, accidents, homicides — and moderate-risk causes like lung cancer from smoking.
….
American men aren’t the only ones dying younger; the life-expectancy gap between men and women exists everywhere in the world. But what is different is that other countries have done much more on a national level to try to make progress in improving men’s health. A handful, including Ireland, Australia and Brazil, have developed national men’s health policies. Since Ireland introduced its strategy in 2008 — the world’s first — it has made considerable strides in male life expectancy, outpacing most European nations. One advance the country has made is at workplaces, getting employers in male-dominated industries, like farming and construction, on board with prioritizing men’s health. “When we started this 20 years ago, we were met with a lot of resistance,” Noel Richardson, a key architect of Ireland’s men’s health plan, told me. “There’s been quite a sea change. There’s a mainstreaming and a normalizing of health for men as something we should all aspire to.”
Author(s): By Helen Ouyang
Helen Ouyang is a physician and contributing writer for the magazine.
Publication Date: 25 Aug 2025
Publication Site: NYT Magazine