Link: https://data.unicef.org/topic/child-survival/under-five-mortality/
Graphic:
Excerpt:
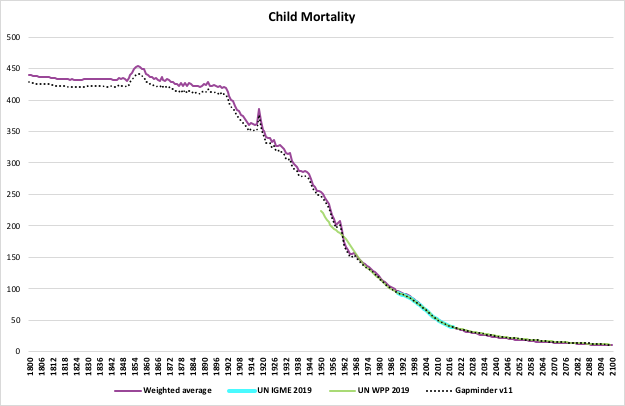
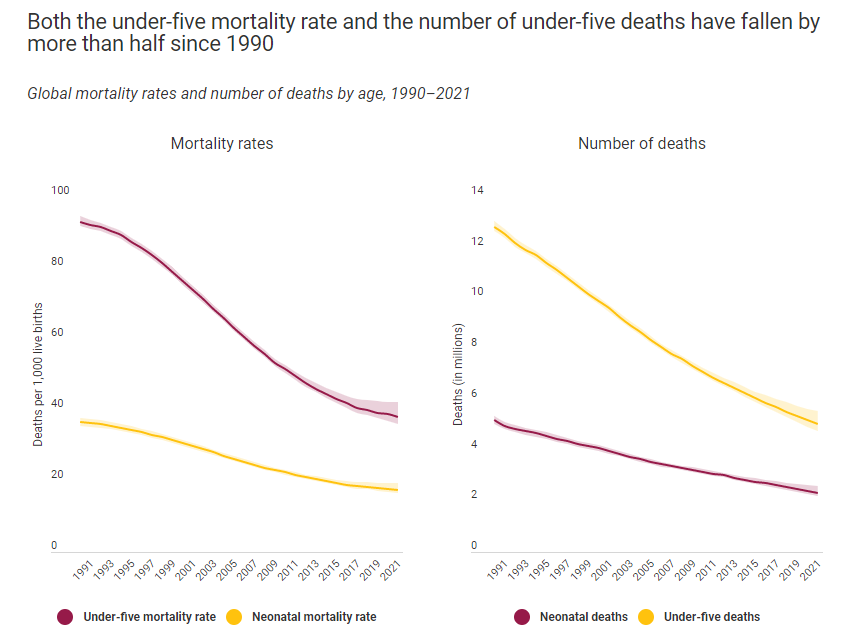
The world made remarkable progress in child survival in the past three decades, and millions of children have better survival chances than in 1990—1 in 26 children died before reaching age five in 2021, compared to 1 in 11 in 1990. Moreover, progress in reducing child mortality rates has been accelerated in the 2000s period compared with the 1990s, with the annual rate of reduction in the global under-five mortality rate increasing from 1.8 per cent in 1990s to 4.0 per cent for 2000-2009 and 2.7 per cent for 2010-2021.
Under-five mortality
The under-five mortality rate refers to the probability a newborn would die before reaching exactly 5 years of age, expressed per 1,000 live births. In 2021, 5.0 million children under 5 years of age died. Globally, infectious diseases, including pneumonia, diarrhoea and malaria, remain a leading cause of under-five deaths, along with preterm birth and intrapartum-related complications.
The global under-five mortality rate declined by 59 per cent, from 93 deaths per 1,000 live births in 1990 to 38 in 2021. Despite this considerable progress, improving child survival remains a matter of urgent concern. In 2021 alone, roughly 13,800 under-five deaths occurred every day, an intolerably high number of largely preventable child deaths.
Publication Date: January 2023, accessed 21 March 2023
Publication Site: UNICEF