Link: https://jnnp.bmj.com/content/early/2025/03/21/jnnp-2024-334925.long
Excerpt:
Abstract
Background At least 60% of stroke, 40% of dementia and 35% of late-life depression (LLD) are attributable to modifiable risk factors, with great overlap due to shared pathophysiology. This study aims to systematically identify overlapping risk factors for these diseases and calculate their relative impact on a composite outcome.
Methods A systematic literature review was performed in PubMed, Embase and PsycInfo, between January 2000 and September 2023. We included meta-analyses reporting effect sizes of modifiable risk factors on the incidence of stroke, dementia and/or LLD. The most relevant meta-analyses were selected, and disability-adjusted life year (DALY) weighted beta (β)-coefficients were calculated for a composite outcome. The β-coefficients were normalised to assess relative impact.
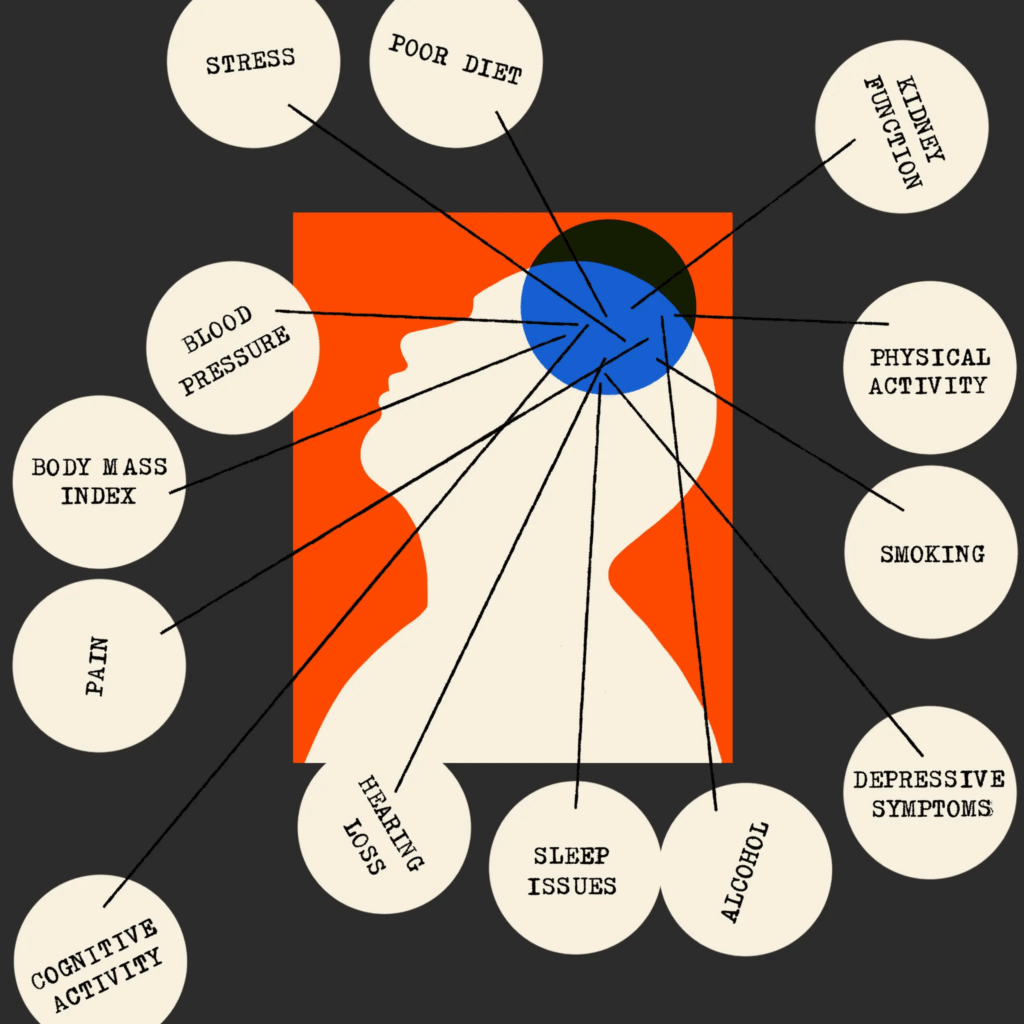
Results Our search yielded 182 meta-analyses meeting the inclusion criteria, of which 59 were selected to calculate DALY-weighted risk factors for a composite outcome. Identified risk factors included alcohol (normalised β-coefficient highest category: −34), blood pressure (130), body mass index (70), fasting plasma glucose (94), total cholesterol (22), leisure time cognitive activity (−91), depressive symptoms (57), diet (51), hearing loss (60), kidney function (101), pain (42), physical activity (−56), purpose in life (−50), sleep (76), smoking (91), social engagement (53) and stress (55).
Conclusions This study identified overlapping modifiable risk factors and calculated the relative impact of these factors on the risk of a composite outcome of stroke, dementia and LLD. These findings could guide preventative strategies and serve as an empirical foundation for future development of tools that can empower people to reduce their risk of these diseases.
https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2024-334925
Publication Date: April 2025
Publication Site: Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, & Psychiatry