Link: https://science.sciencemag.org/content/early/2021/05/19/science.abg6296
Graphic:
Abstract:
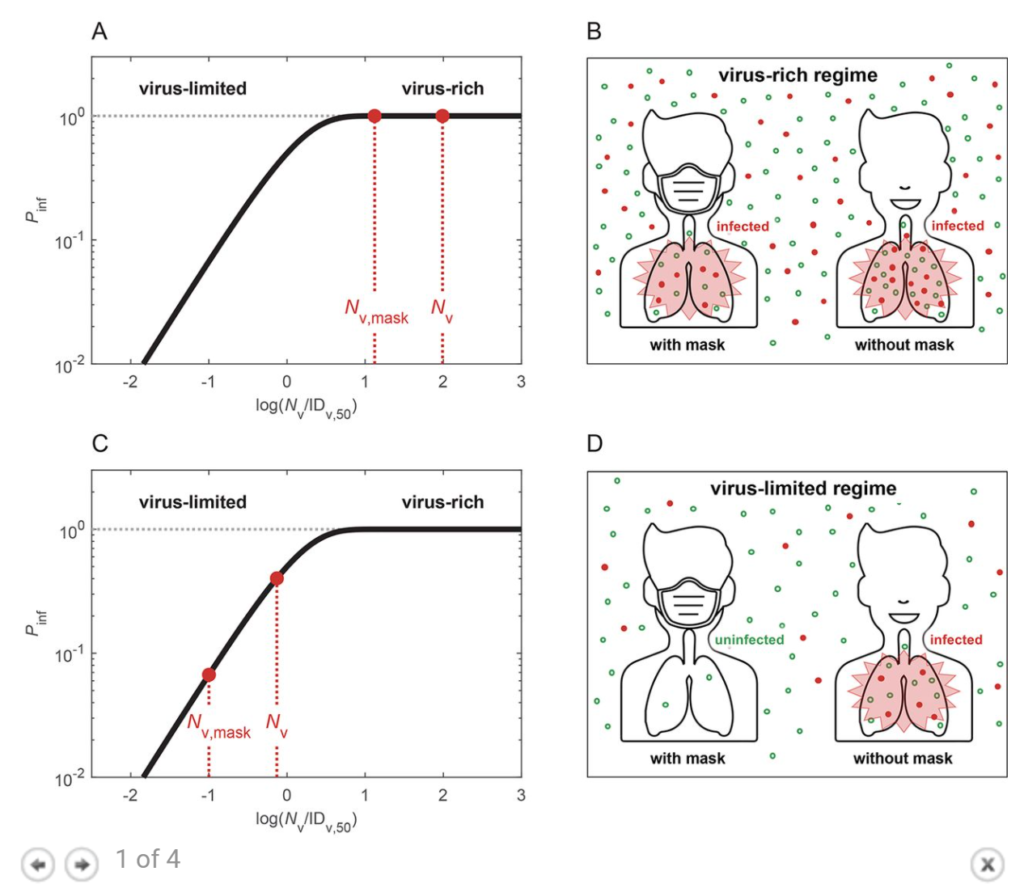
Airborne transmission by droplets and aerosols is important for the spread of viruses. Face masks are a well-established preventive measure, but their effectiveness for mitigating SARS-CoV-2 transmission is still under debate. We show that variations in mask efficacy can be explained by different regimes of virus abundance and related to population-average infection probability and reproduction number. For SARS-CoV-2, the viral load of infectious individuals can vary by orders of magnitude. We find that most environments and contacts are under conditions of low virus abundance (virus-limited) where surgical masks are effective at preventing virus spread. More advanced masks and other protective equipment are required in potentially virus-rich indoor environments including medical centers and hospitals. Masks are particularly effective in combination with other preventive measures like ventilation and distancing.
Author(s): Yafang Cheng, Nan Ma, Christian Witt, Steffen Rapp, Philipp S. Wild, Meinrat O. Andreae, Ulrich Pöschl, Hang Su
Publication Date: 20 May 2021
Publication Site: Science