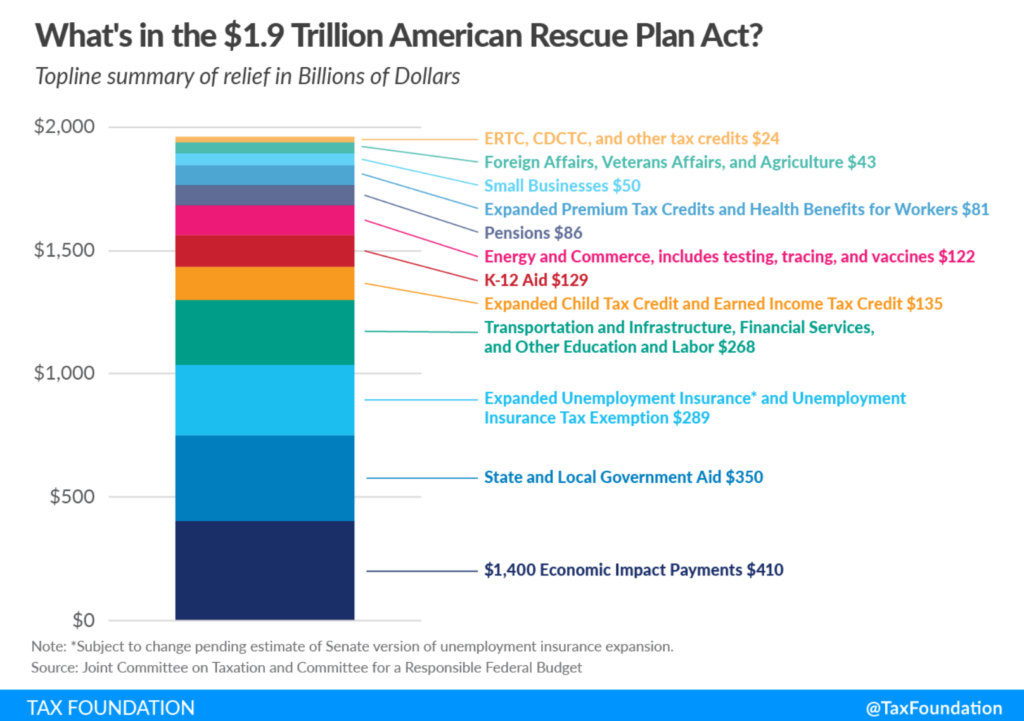
Graphic:
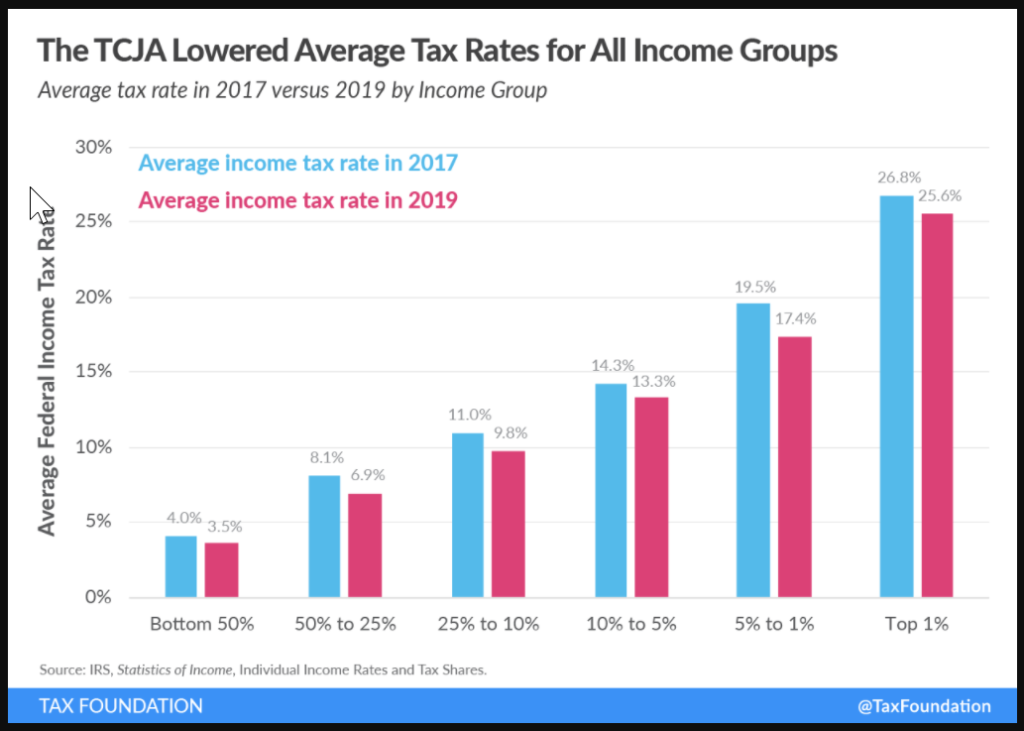
Excerpt:
In 2019, taxpayers filed 148.3 million tax returns, reported earning nearly $11.9 trillion in adjusted gross income, and paid $1.6 trillion in individual income taxes.
The top 1 percent of taxpayers paid a 25.6 percent average individual income tax rate, which is more than seven times higher than taxpayers in the bottom 50 percent (3.5 percent).
The share of reported income earned by the top 1 percent of taxpayers fell to 20.1 percent from 20.9 percent in 2018. The top 1 percent’s share of federal individual income taxes paid fell to 38.8 percent from 40.1 percent.
The top 50 percent of all taxpayers paid 97 percent of all individual income taxes, while the bottom 50 percent paid the remaining 3 percent.
The top 1 percent paid a greater share of individual income taxes (38.8 percent) than the bottom 90 percent combined (29.2 percent).
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act reduced average tax rates across income groups.
Author(s): Erica York
Publication Date: 19 Jan 2022
Publication Site: Tax Foundation