Link: https://reason.com/2022/10/27/the-experts-were-never-going-to-fix-inflation/
Excerpt:
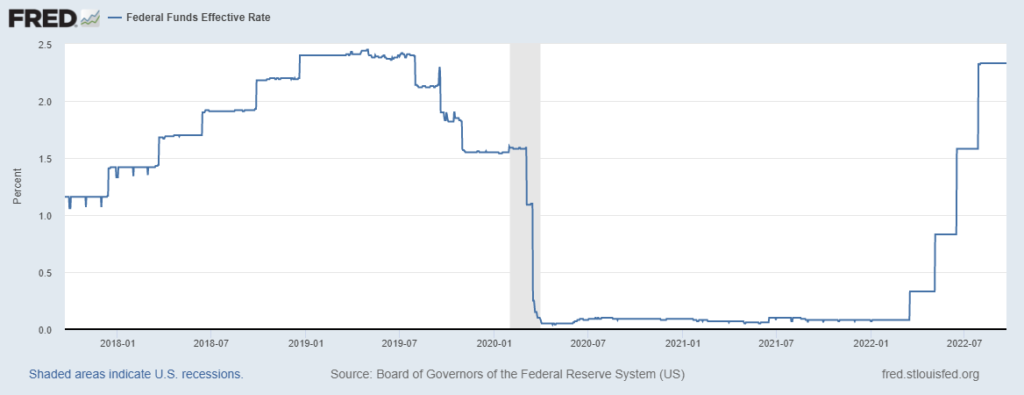
Debate now rages about whether the Federal Reserve should continue to raise interest rates to tame inflation or slow down these hikes and see what happens. This is not the first debate we’ve had recently about inflation and Fed actions. The lesson we should learn, and I fear we won’t, is that government officials and those advising them from inside or outside the government don’t know as much as they claim to about the interventions they design to control the economy.
As a reminder, in 2021, the dominant voices including Fed Chairman Jerome Powell asserted that the emerging inflation would be “transitory” and disappear when pandemic-induced supply constraints dissolve. That was wrong. When this fact became obvious, the messaging shifted: Fed officials could and would fight inflation in a timely manner by raising rates to the exact level needed to avoid recession and higher unemployment. Never mind that the whole point of raising interest rates is precisely to soak money out of the economy by slowing demand, which often causes unemployment to rise.
…..
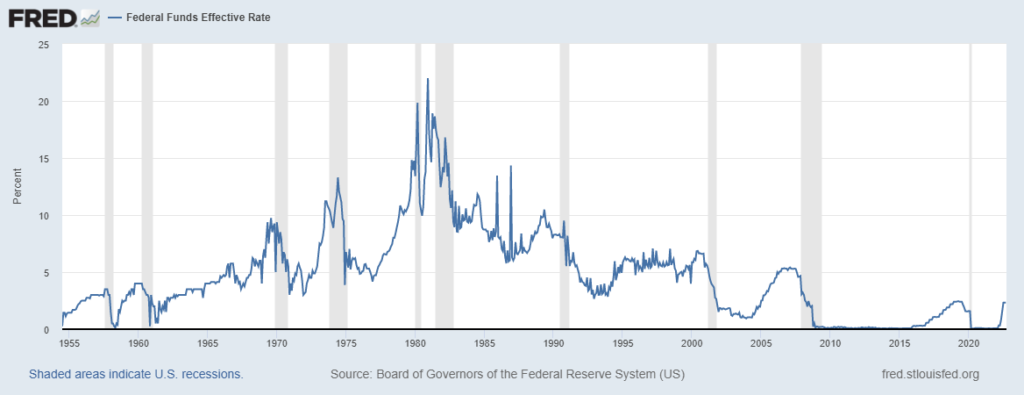
Over at Discourse magazine, my colleague Thomas Hoenig—a former president of the Fed’s Kansas City branch—explains how Fed officials faced similar pressures during the late 1960s and 1970s. Unfortunately, he writes, “Bowing to congressional and White House pressure, [Fed officials] held interest rates at an artificially low level….What followed was a persistent period of steadily higher inflation, from 4.5% in 1971 to 14% by 1980. Only then did the [Federal Reserve Open Market Committee], under the leadership of Paul Volcker, fully address inflation.”
Often overlooked is Volcker’s accomplishment: the willingness to stay the course despite a painful recession. Indeed, it took about three years from when he pushed interest rates up to about 20 percent in 1979 for the rate of inflation to fall to a manageable level. As such, Hoenig urges the Fed to stay strong today. He writes, “Interest rates must rise; the economy must slow, and unemployment must increase to regain control of inflation and return it to the Fed’s 2% target.” There is a cost in doing this; a soft landing was never in the cards.
Author(s): VERONIQUE DE RUGY
Publication Date: 27 Oct 2022
Publication Site: Reason