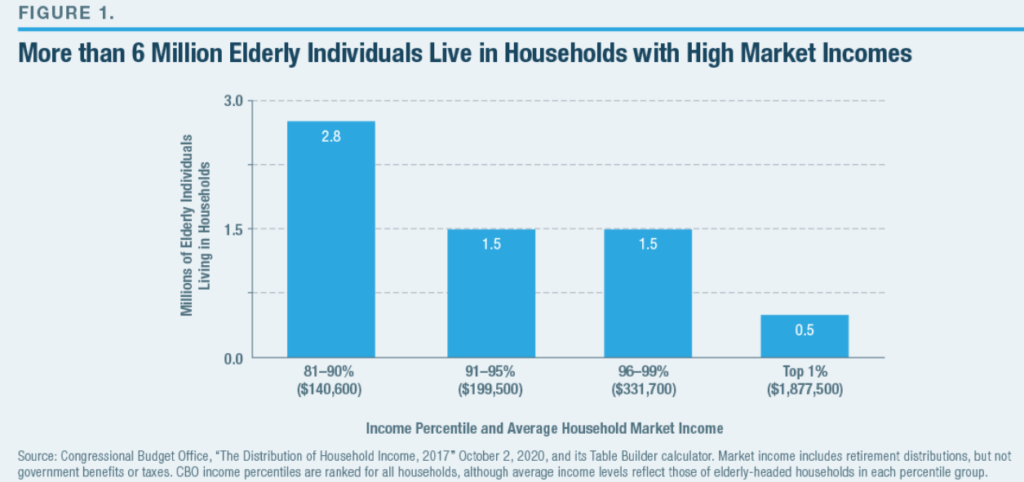
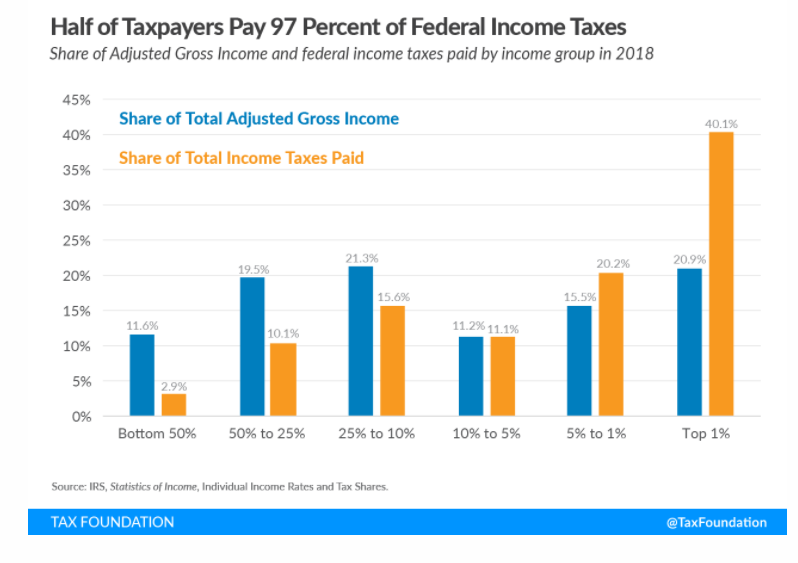
Link:https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/pdf/R/R44641
Graphic:
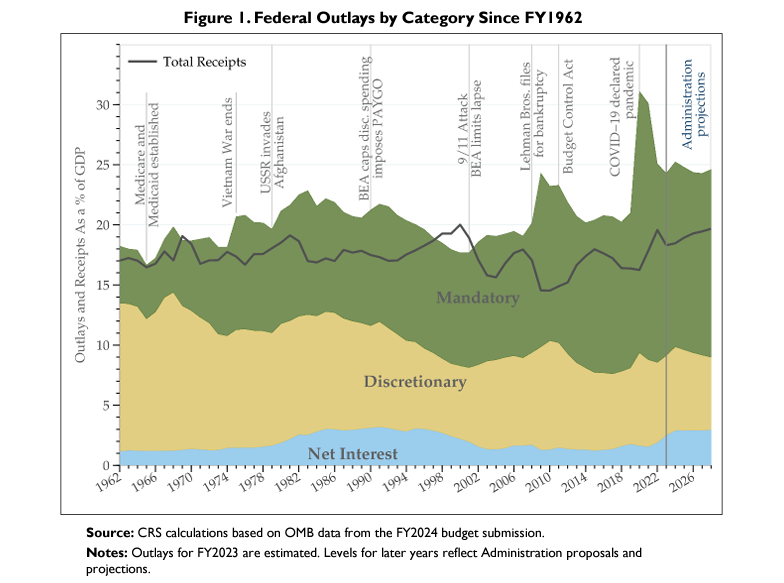
Excerpt:
In FY2023, mandatory spending accounts for an estimated 63% of total federal spending. Social Security alone accounts for about 21% of federal spending. Medicare and the federal share of Medicaid together account for another 25% of federal spending. Therefore, spending on Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid now makes up almost half of total federal spending.
These figures do not reflect the implicit cost of tax expenditures, which are revenue losses attributable to provisions of the federal tax laws that allow a special exclusion, exemption, or deduction from gross income or provide a special credit, a preferential tax rate, or a deferral of tax liability.8 As with mandatory spending, tax policy is not controlled by annual appropriations acts, but by other types of legislation.
Author(s): Congressional Research Service
Publication Date: last updated 7 Nov 2023
Publication Site: U.S. Congress