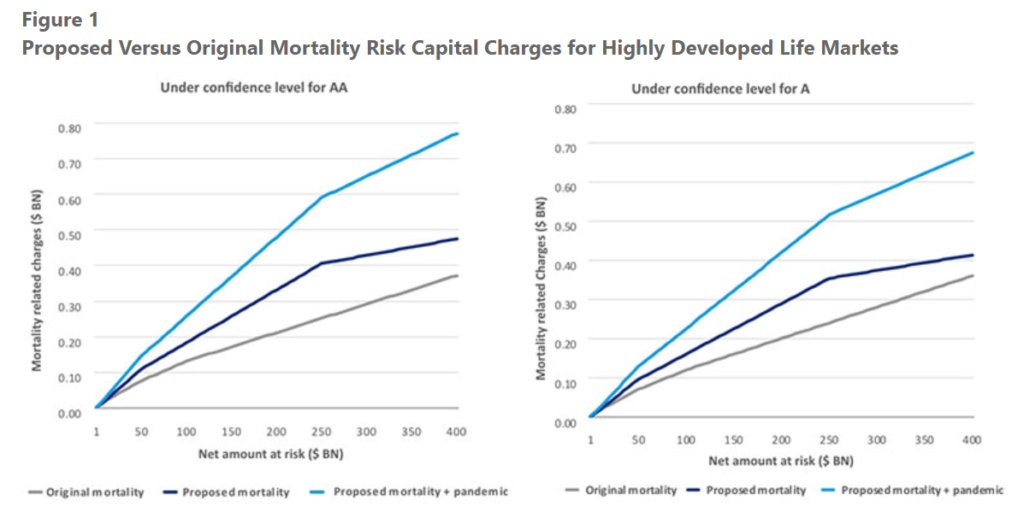
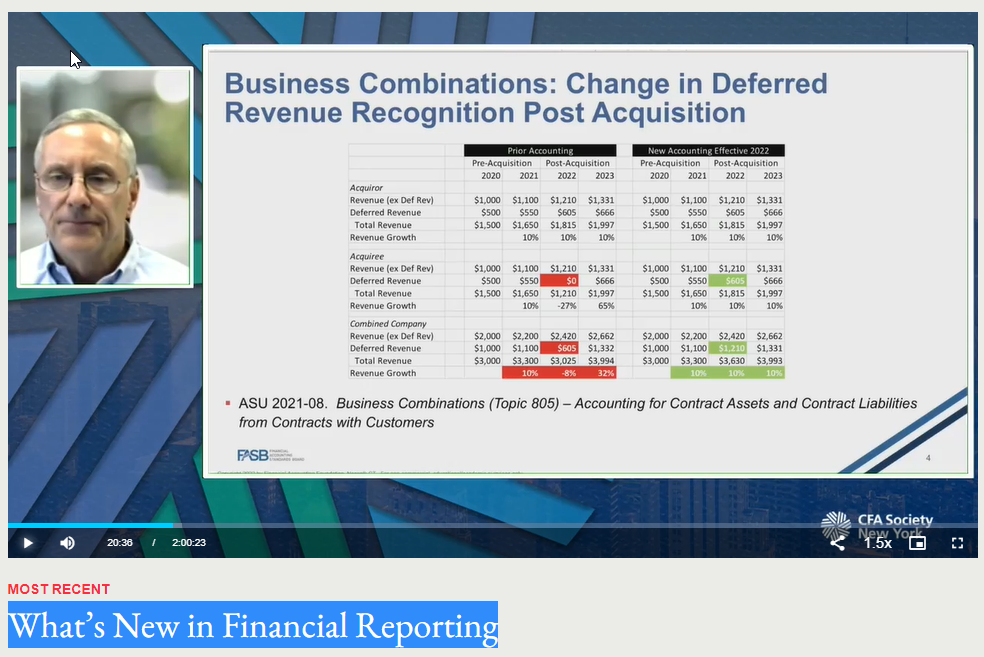
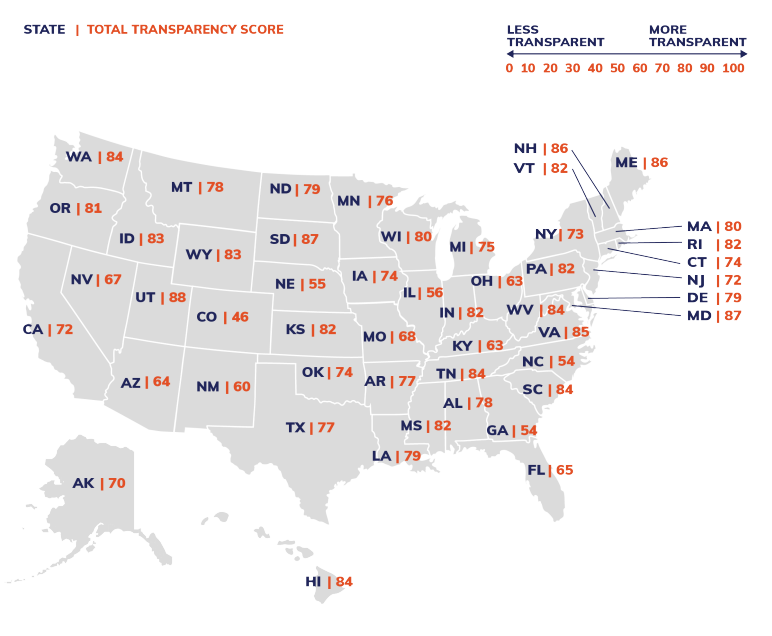
Excerpt:
planadvisor.com reports:
Department of Labor Inspector General Larry Turner issued a semi-annual report Tuesday arguing that the Employee Benefit Security Administration lacks both the resources and authority to fulfill its mandate to employee benefit plans. The report particularly emphasized EBSA’s limited authority to conduct thorough audits of workplace retirement plans.
My takeaways from the report:
The OIG remains concerned about the Employee Benefits Security Administration’s (EBSA) ability to protect the integrity of pension, health, and other benefit plans of about 153 million workers, retirees, and their families under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (ERISA). In particular, the OIG is concerned about the statutory limitations on EBSA’s oversight authority and inadequate resources to conduct compliance and enforcement. A decades-long challenge to EBSA’s compliance program, ERISA provisions allow billions of dollars in pension assets to escape full audit scrutiny. The act generally requires every employee benefit plan with more than 100 participants to obtain an audit of the plan’s financial statements each year. However, an exemption in the law allowed auditors to perform “limited-scope audits.” These audits excluded pension plan assets already certified by certain banks or insurance carriers and provided little to no confirmation regarding the actual existence or value of the assets. (page 23)
Author(s): John Bury
Publication Date: 6 Dec 2023
Publication Site: burypensions