Link: https://fixedincome.fidelity.com/ftgw/fi/FINewsArticle?id=202106081343SM______BNDBUYER_00000179-ec17-d1ac-a5fb-ef37eda90001_110.1
Excerpt:
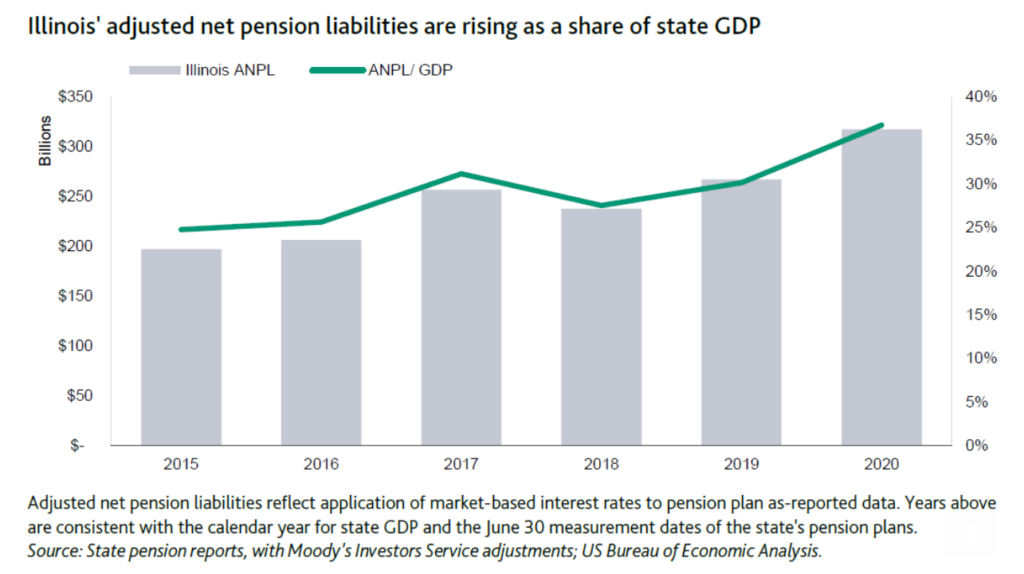
The Chicago Park District pension funding overhaul approved by lawmakers moves the fund off a path to insolvency to a full funding target in 35 years, with bonding authority.
State lawmakers approved the statutory changes laid out in House Bill 0417 on Memorial Day before adjourning their spring session and Gov. J.B. Pritzker is expected to sign it. It puts the district?s contributions on a ramp to an actuarially based payment, shifting from a formula based on a multiplier of employee contributions. The statutory multiplier formula is blamed for the city and state?s underfunded pension quagmires.
“There are number of things here that are really, really good,? Sen. Robert Martwick, D-Chicago, told fellow lawmakers during a recent Senate Pension Committee hearing. Martwick is a co-sponsor of the legislation and also heads the committee.
?This is a measure that puts the district on to a path to full funding over the course of 35 years,” he said. “It is responsible. There is no opposition to it. This is exactly more of what we should be doing.”
The district will ramp up to an actuarially based contribution beginning this year when 25% of the actuarially determined contribution is owed, then half in 2022, and three-quarters in 2023 before full funding is required in 2024. To help keep the fund from sliding backwards during the ramp period the district will deposit an upfront $40 million supplemental contribution.
The 35-year clock will start last December 31 to reach the 100% funded target by 2055.
Author(s): Yvette Shields
Publication Date: 8 June 2021
Publication Site: Fidelity Fixed Income