Link:https://academic.oup.com/ije/advance-article/doi/10.1093/ije/dyab207/6375510
Graphic:

Abstract:
Background
Variations in the age patterns and magnitudes of excess deaths, as well as differences in population sizes and age structures, make cross-national comparisons of the cumulative mortality impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic challenging. Life expectancy is a widely used indicator that provides a clear and cross-nationally comparable picture of the population-level impacts of the pandemic on mortality.Methods
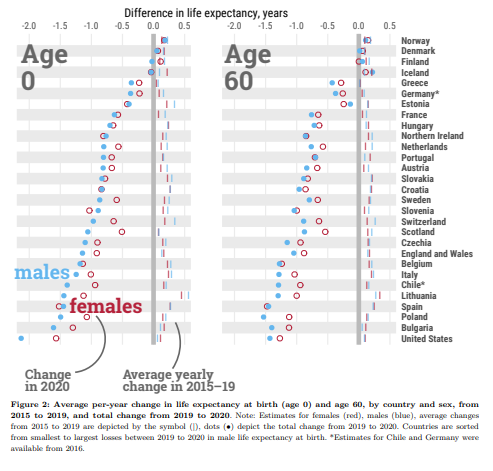
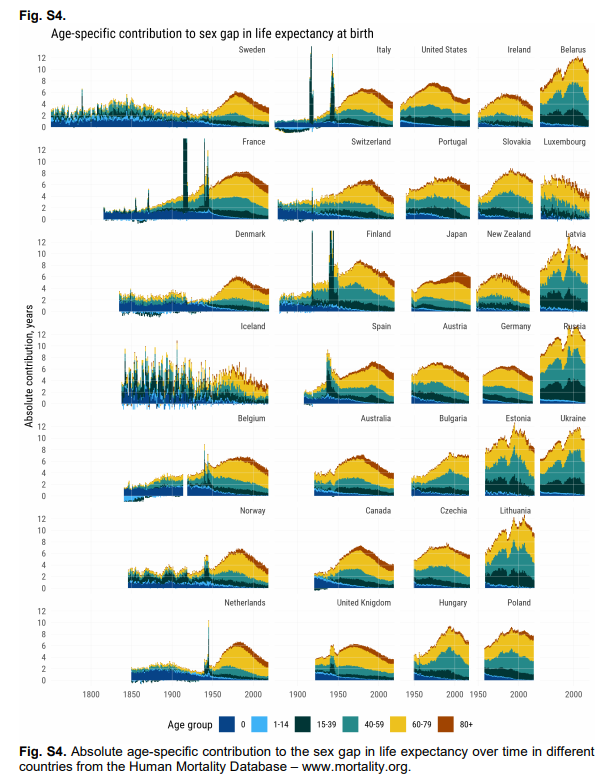
Life tables by sex were calculated for 29 countries, including most European countries, Chile and the USA, for 2015–2020. Life expectancy at birth and at age 60 years for 2020 were contextualized against recent trends between 2015 and 2019. Using decomposition techniques, we examined which specific age groups contributed to reductions in life expectancy in 2020 and to what extent reductions were attributable to official COVID-19 deaths.Results
Life expectancy at birth declined from 2019 to 2020 in 27 out of 29 countries. Males in the USA and Lithuania experienced the largest losses in life expectancy at birth during 2020 (2.2 and 1.7 years, respectively), but reductions of more than an entire year were documented in 11 countries for males and 8 among females. Reductions were mostly attributable to increased mortality above age 60 years and to official COVID-19 deaths.Conclusions
The COVID-19 pandemic triggered significant mortality increases in 2020 of a magnitude not witnessed since World War II in Western Europe or the breakup of the Soviet Union in Eastern Europe. Females from 15 countries and males from 10 ended up with lower life expectancy at birth in 2020 than in 2015.
Author(s): José Manuel Aburto, Jonas Schöley, Ilya Kashnitsky, Luyin Zhang, Charles Rahal, Trifon I Missov, Melinda C Mills, Jennifer B Dowd, Ridhi Kashyap
Publication Date: 26 Sept 2021
Publication Site: International Journal of Epidemiology