Graphic:
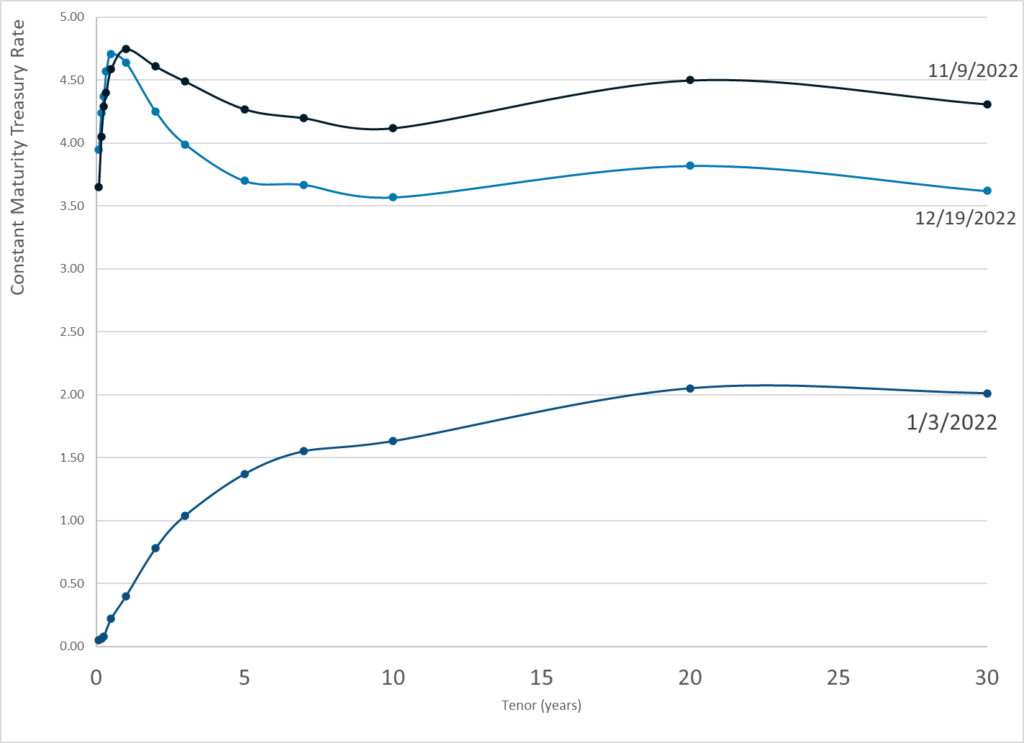
Publication Date: 19 Dec 2022
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
All about risk
Graphic:

Publication Date: 19 Dec 2022
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Link: https://content.naic.org/research_moody.htm
Historical record: https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1Sgi6XVzK0_sCtAWuCnUD02eObOTC3S4xlQgMep32OeU/edit?usp=sharing
Graphic:
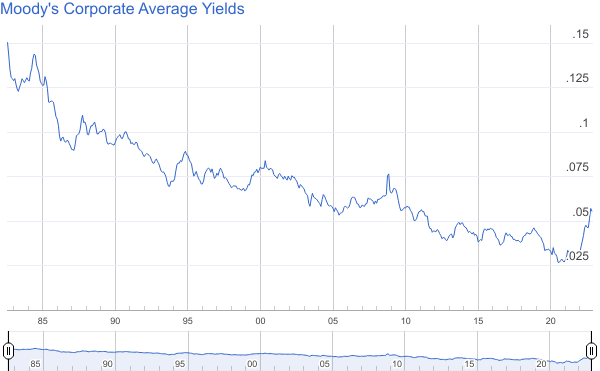
Publication Date: accessed 9 Dec 2022
Publication Site: NAIC
Graphic:
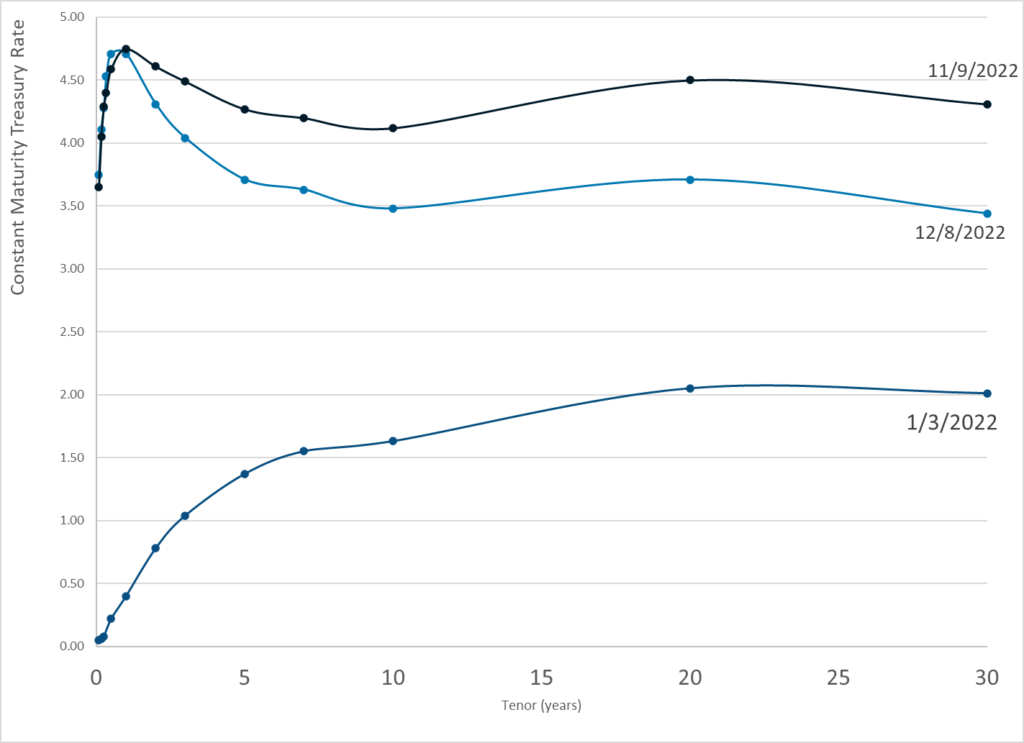
Publication Date: 8 Dec 2022
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Graphic:
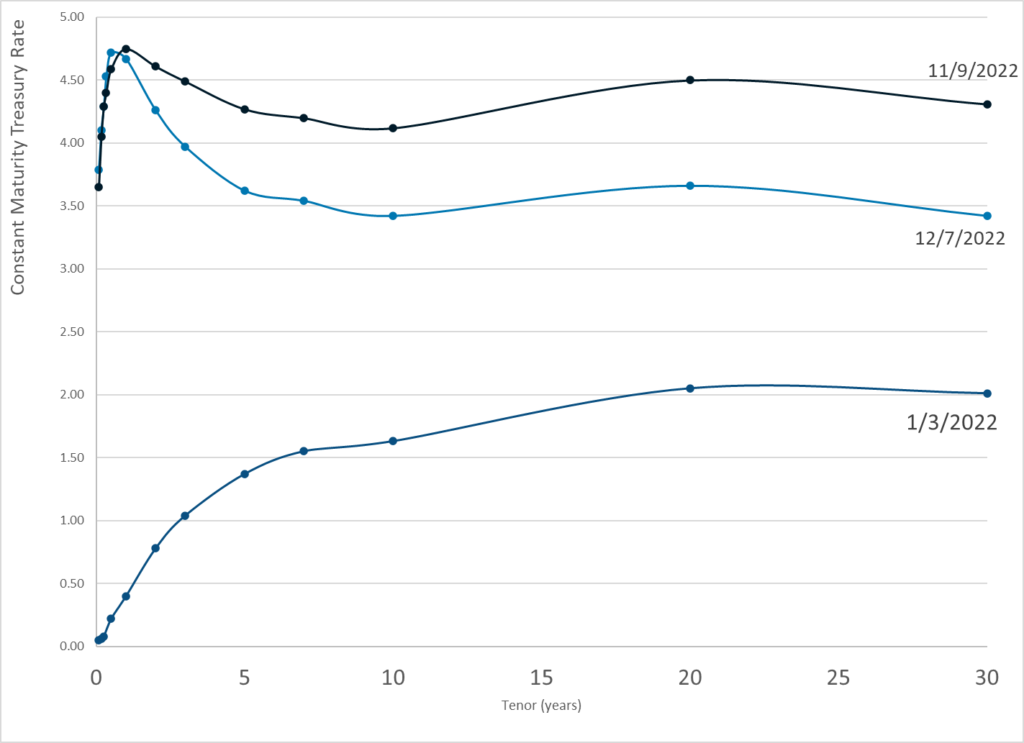
Publication Date: 7 Dec 2022
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Graphic:
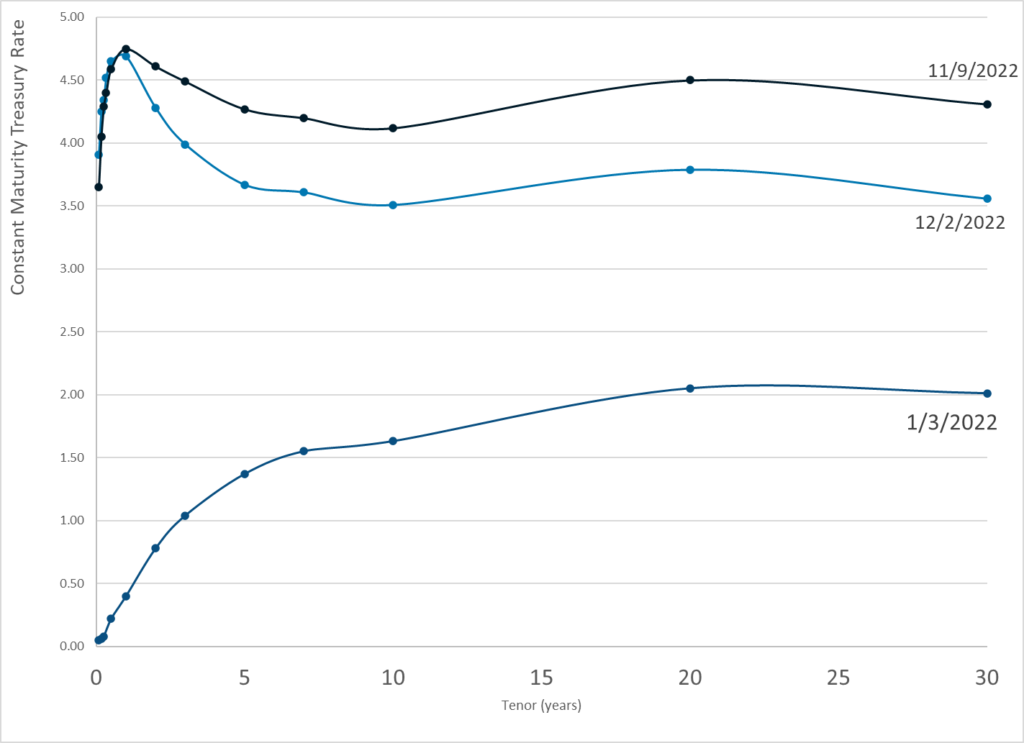
Publication Date: 2 Dec 2022
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Graphic:
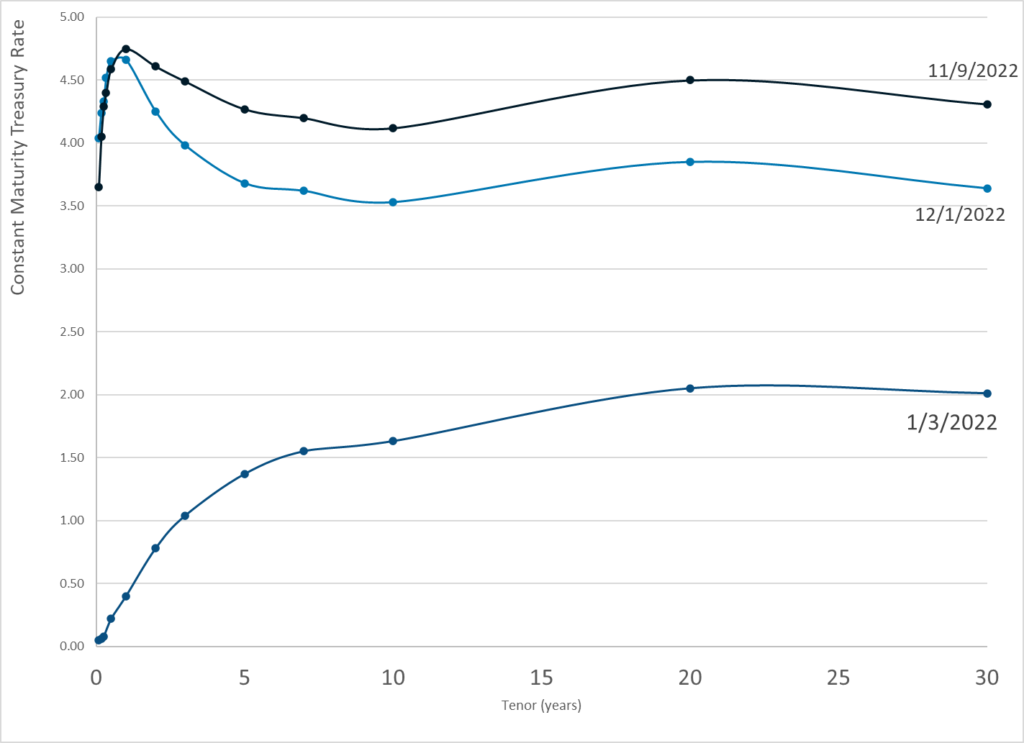
Publication Date: 1 Dec 2022
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Graphic:
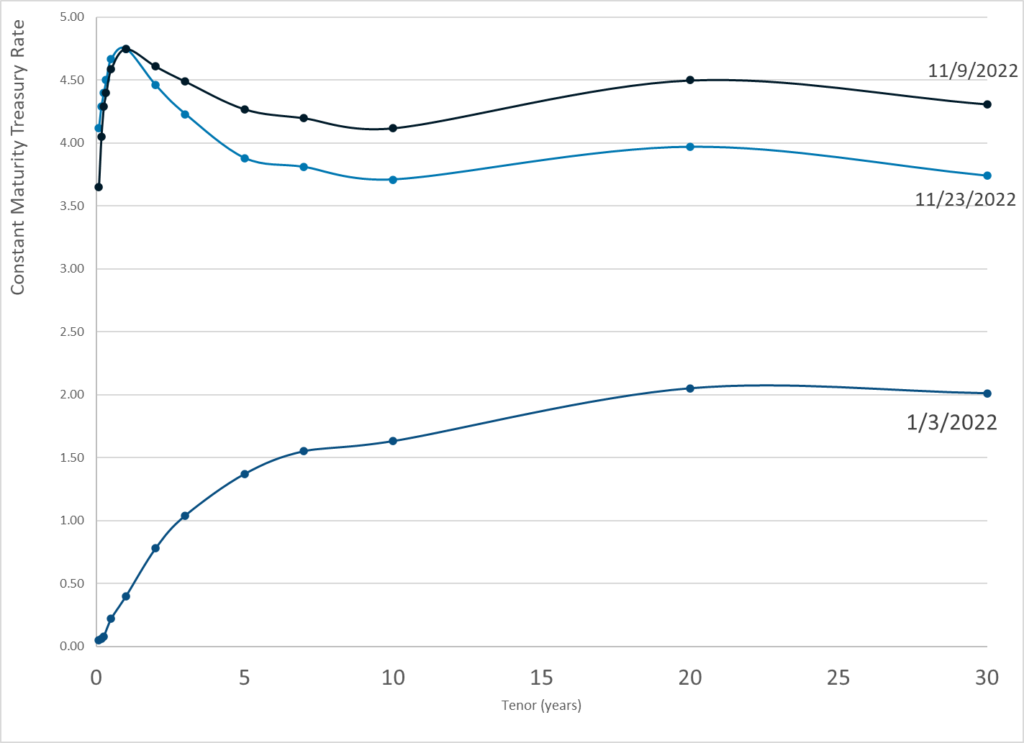
:
Publication Date: 23 Nov 2022
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Graphic:
Publication Date: 16 Nov 2022
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Graphic:
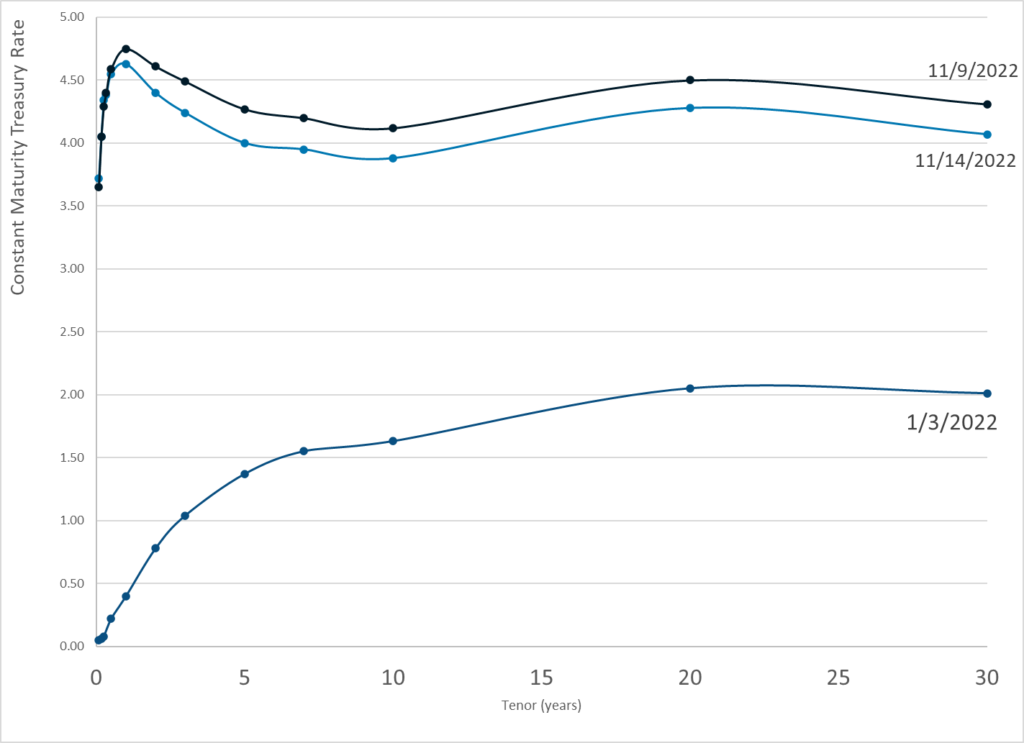
Publication Date: 14 Nov 2022
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Graphic:
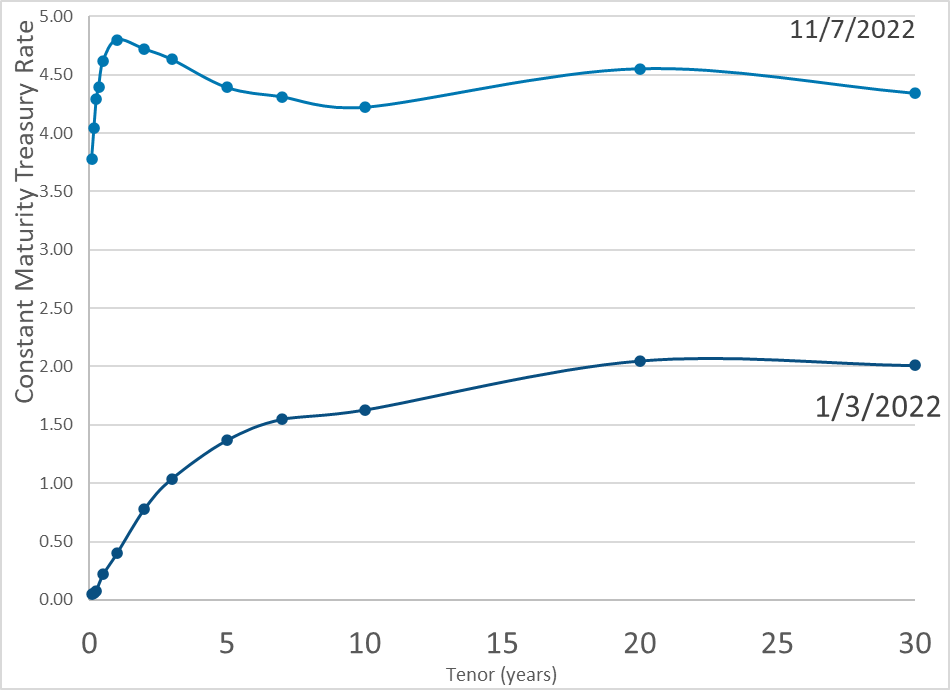
Publication Date: 7 Nov 2022
Publication Site: Treasury Dept
Graphic:
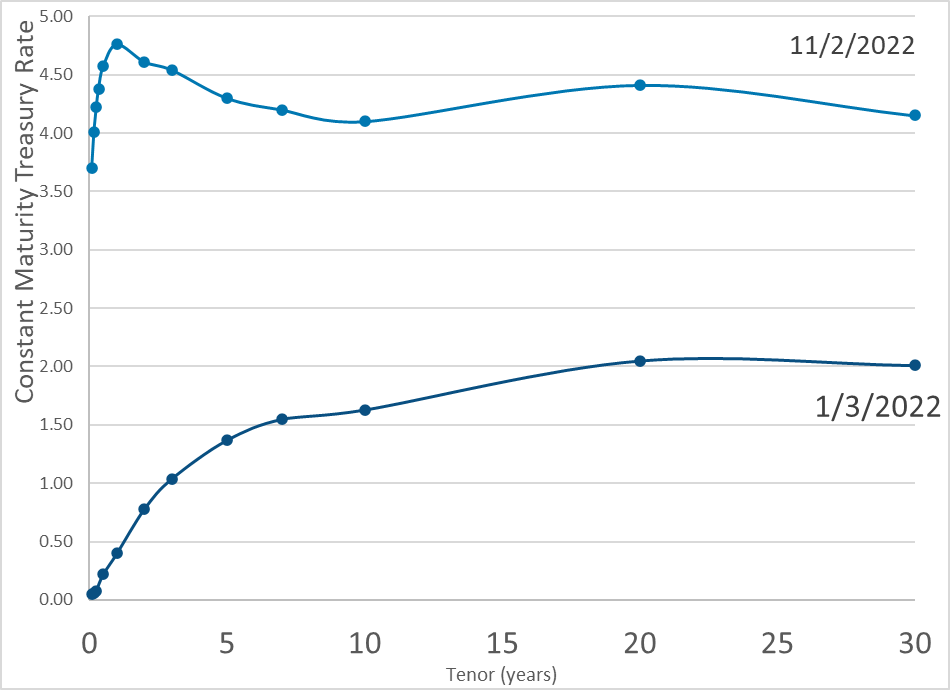
Publication Date: 2 Nov 2022
Publication Site: Dept of Treasury
Graphic:
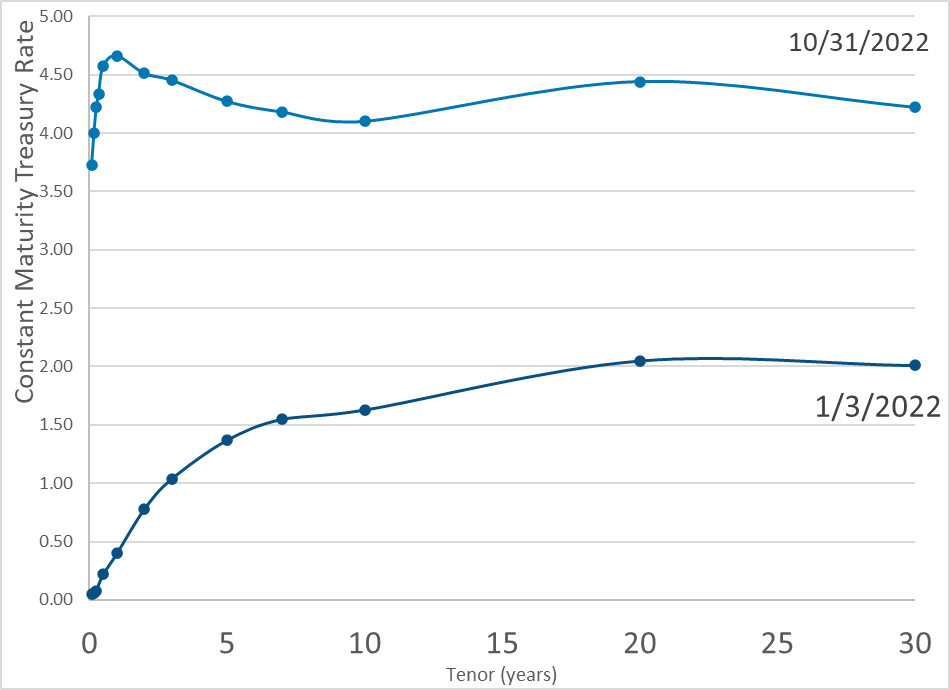
Publication Date: 31 Oct 2022
Publication Site: Treasury Dept