Graphic:
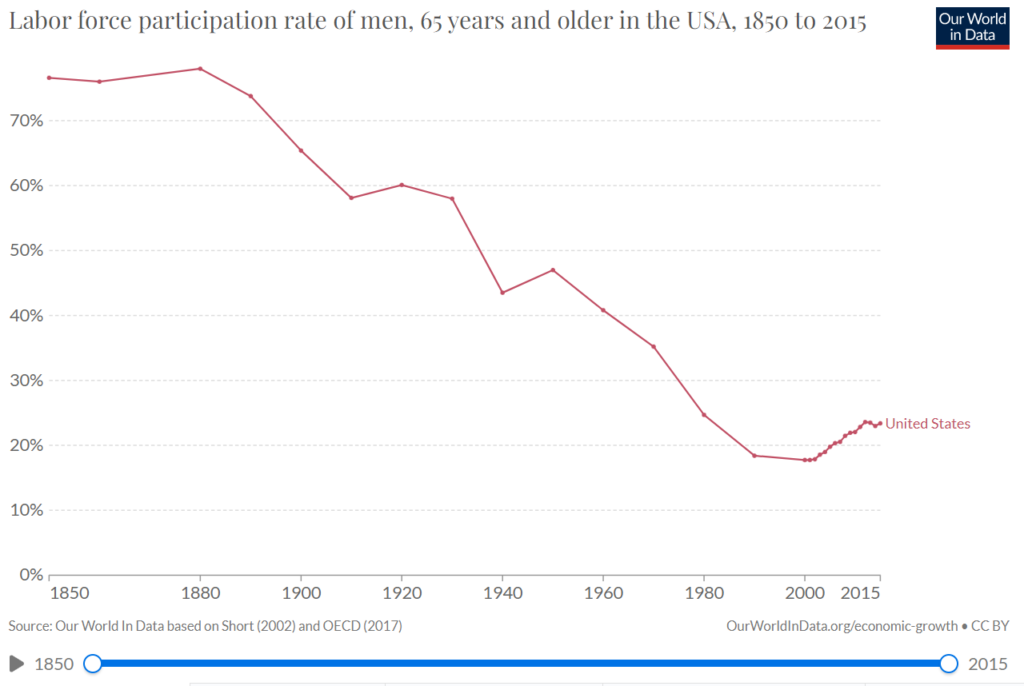
Publication Date: accessed 18 April 2023
Publication Site: Our World in Data
All about risk
Graphic:

Publication Date: accessed 18 April 2023
Publication Site: Our World in Data
Graphic:
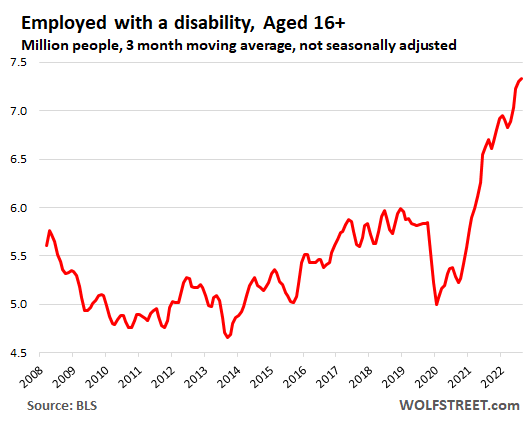
Excerpt:
The number of people with a disability who were employed in January spiked by 27% from January 2020, to 7.29 million in January — with December at 7.37 million having been the highest in the data from the BLS going back to 2008:
Author(s): Wolf Richter
Publication Date: 3 Feb 2023
Publication Site: Wolf Street
Graphic:
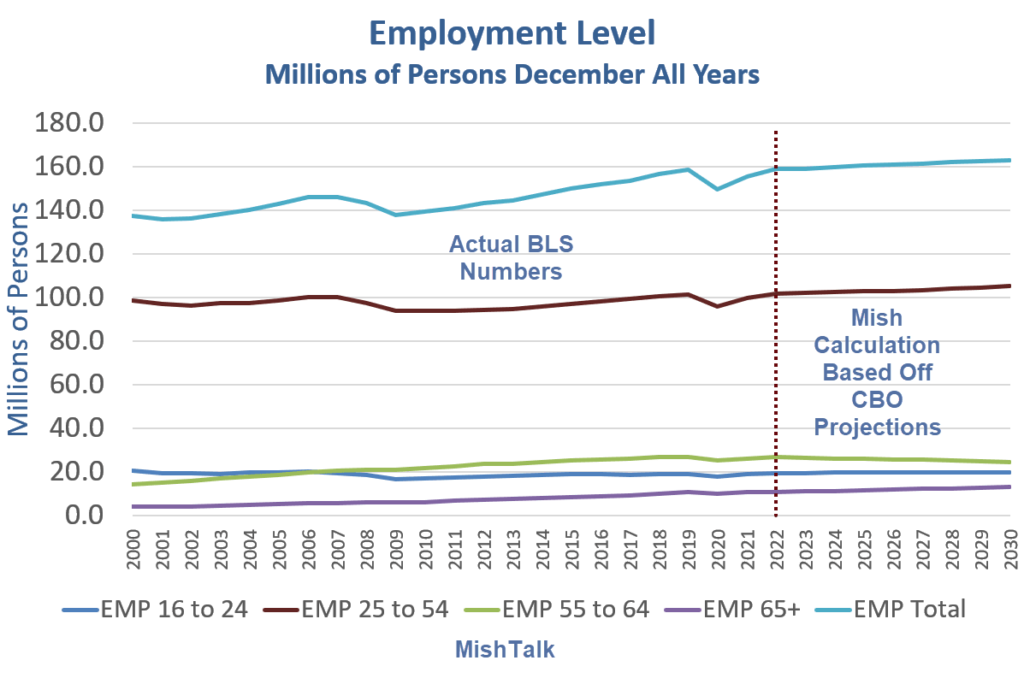
Excerpt:
If you work one hour, you are employed. If you don’t have a job and fail to look for one, you are not considered unemployed, rather, you drop out of the labor force.
Looking for job openings on Jooble or Monster or in the want ads does not count as “looking for a job”. You need an actual interview or send out a resume.
These distortions artificially lower the unemployment rate, artificially boost full-time employment, and artificially increase the payroll jobs report every month.
Q&A What’s Going On?
Q: Hey Mish, What’s Going On?
A: People are taking on second part time jobs to make ends meet. But full time employment is stagnant no matter how one slices and dices the revisions.
Author(s): Mike Shedlock
Publication Date: 3 Feb 2023
Publication Site: Mish Talk
Graphic:
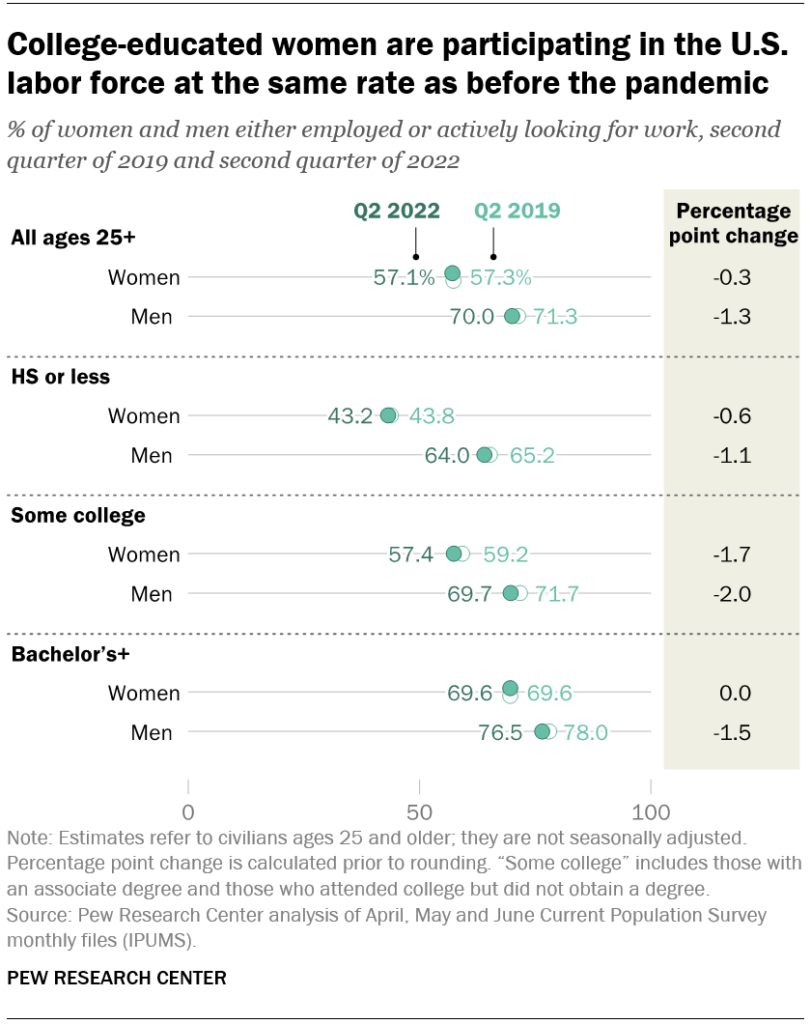
Excerpt:
In the second quarter of 2022, the labor force participation rate for college-educated women was 69.6%, the same as in the second quarter of 2019. In contrast, men and most other educational groups now have lower rates of labor force participation than they did in the second quarter of 2019.
This shift in the college-educated labor force – as women now comprise a majority – comes around four decades after women surpassed men in the number of Americans earning a bachelor’s degree each year.
Author(s): Richard Fry
Publication Date: 26 Sept 2022
Publication Site: Pew Research Center
Link: https://siepr.stanford.edu/publications/working-paper/impacts-covid-19-illnesses-workers
Graphic:
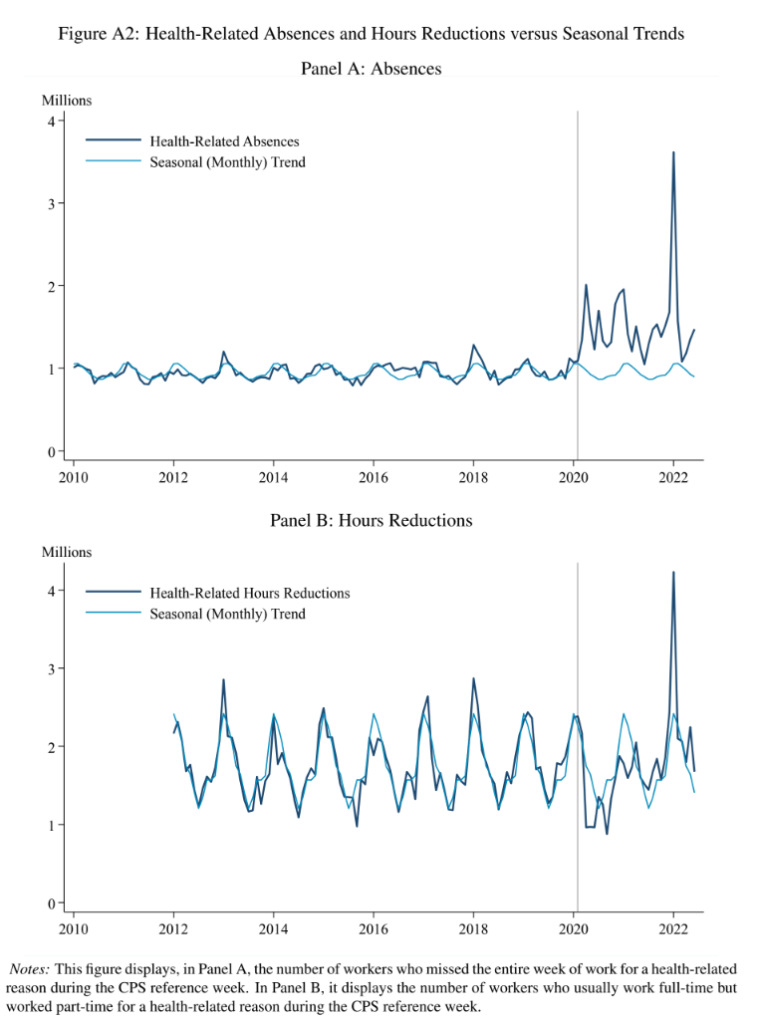
Excerpt:
We show that Covid-19 illnesses persistently reduce labor supply. Using an event study, we estimate that workers with week-long Covid-19 work absences are 7 percentage points less likely to be in the labor force one year later compared to otherwise-similar workers who do not miss a week of work for health reasons. Our estimates suggest Covid-19 illnesses have reduced the U.S. labor force by approximately 500,000 people (0.2 percent of adults) and imply an average forgone earnings per Covid-19 absence of at least $9,000, about 90 percent of which reflects lost labor supply beyond the initial absence week.
Author(s):
Gopi Shah Goda
Evan J. Soltas
Publication Date: Sept 2022
Publication Site: Stanford University, Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research (SIEPR)
Link: https://www.magnifymoney.com/news/working-older-adults-study/
Excerpt:
Amid the coronavirus pandemic, a rising share of adults 65 and older are working. In late April and early May 2020, 19.5% of Americans 65 and older were working. That figure jumped more than 2 percentage points in late April and early May 2022 to 21.9%. At the same time, the share of U.S. adults who reported that they’re retired is up similarly — from 14.9% in April and May 2020 to 17.4% in April and May 2022.
More than a quarter of working Americans 65 and older are self-employed. 25.6% of employed older Americans are self-employed — more than triple the rate among working Americans 25 to 39. Meanwhile, the government isn’t the landing spot it once was for older workers: In April and May 2020, 15.2% of employed Americans 65 and older worked for the government. In April and May 2022, however, that percentage plummeted by a third to 10.1%.
New Jersey saw the largest jump in older adults in the workforce since the beginning of the pandemic. In April and May 2020, 18.1% of Americans 65 and older were employed in New Jersey. By April and May 2022, that was up 18.9 percentage points to 37.0%. The other states with double-digit increases were West Virginia (17.2 percentage points) and Pennsylvania (14.6).
North Dakota saw the biggest dip in the percentage of adults 65 and older in the workforce. The rate of older working adults went from 36.0% in April and May 2020 to 25.0% in April and May 2022 — a drop of 11.0 percentage points. Other big drops were seen in Wisconsin (8.3 percentage points) and North Carolina (6.3).
Author(s): Alex Cook
Publication Date: 6 Jun 2022
Publication Site: Magnify Money
Excerpt:
The research showed that the rate at which older workers left employment increased dramatically during the pandemic.
This was especially the case with women — an 8-percentage-point increase vs. 7 points for men; Asian Americans — a 13-point increase; those with less than a college degree — a 10-point increase; and workers with occupations that did not lend themselves to remote work.
….
There was one exception: Workers 70 and older were 5.9 percentage points more likely to leave the workforce and retire. The study noted that these workers were likely already receiving Social Security benefits, so claiming did not markedly increase.
Among all workers 55 and older, the monthly claiming rate for Social Security benefits remained constant between April 2019 and June 2021, the researchers found.
Author(s): Michael S. Fischer
Publication Date: 30 Dec 2021
Publication Site: Think Advisor
Link:https://www.cbsnews.com/news/retirement-covid-pandemic-unretire-labor-shortage/
Excerpt:
An economist will tell you it’s a hot labor market: A record number of people quit their jobs in September, and the U.S. is seeing record job openings as the economy chugs back to life from the coronavirus pandemic. The pandemic drove millions of workers into early retirement — and experts say they could be key to reviving the economy.
The number of people who retired rose much faster than the typical pace during the pandemic. More than 3 million additional people retired compared with normal, a Federal Reserve Bank of Saint Louis analysis found. Meanwhile, the economy is still down nearly 4 million jobs from before COVID-19.
“40% of the older workers that were pushed out of the labor market because they were unemployed, they were laid off, they were fired during the pandemic, 40% of them were permanent job losers and most of them said OK, I’m not just a discouraged worker, I’m not a long-term unemployed, I’m going to tell the [Labor Department] survey I’m retired,'” said Teresa Ghilarducci, labor economist and professor at The New School.
….
But even if retirees return to work at the average pre-pandemic pace, it will take more than two years to bounce back from the recent surge in retirements, the Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas found.
Last month, employment among workers 55 and older increased while unemployment dropped slightly. Older workers are typically more likely to face long-term unemployment than younger workers. While long-term unemployment among older workers changed little last month, it has declined in recent months. Older Americans coming out of retirement might not be returning to the same landscape.
Author(s): Sarah Ewall-Wice
Publication Date: 8 Dec 2021
Publication Site: CBS News
Link: https://www.city-journal.org/government-policies-keeping-women-out-of-workforce
Excerpt:
Since last winter, 1.8 million women have left the labor force entirely—neither working nor looking for work. At first, closed schools and the high cost of child-care options seemed responsible. But economists who have crunched the numbers argue that closed schools can’t explain higher female unemployment. Women with young children make up only 12 percent of the labor force and were only slightly more likely to leave the labor force than were women without young children. The exception? Women with young children who don’t hold college degrees—they constitute only 6 percent of the labor force but saw the biggest drop in employment. Their employment rate has fallen by almost eight percentage points since the pandemic started.
This suggests that women aren’t working for various reasons. For most families, several factors—child-care options, how much a given job will pay, and their partner’s employment prospects—determine whether they will decide to return to work. Rarely in economics does a single cause explain a phenomenon; policies often affect behavior on the margins. If you’re struggling to find good, affordable child care and you are being paid more to stay at home, that extra factor can tip the scales.
Indeed, several current policies seem to be discouraging women from returning to work.
Author(s): Allison Schrager
Publication Date: 15 June 2021
Publication Site: City Journal
Link: https://www.wsj.com/articles/labor-shortage-draws-attention-of-u-s-lawmakers-11622712602
Excerpt:
Congressional lawmakers from both parties are considering incentives such as providing federal funding to pay for hiring bonuses for workers and expanded tax credits for employers. A handful of states are moving to implement such programs on their own, without waiting for Washington.
Some economists, Republican lawmakers and business owners say enhanced federal unemployment benefits are contributing to the labor shortage, because many workers receive more in government aid than they would get on the job. Those benefits — $300 a week on top of regular state payments — are due to expire after Labor Day.
Other economists say the payments have provided a boost to many lower-income families, who have disproportionately lost jobs in the coronavirus pandemic, while in turn pushing money back into the broader economy.
Author(s): Kate Davidson
Publication Date: 3 June 2021
Publication Site: Wall Street Journal
Graphic:

Excerpt:
The U.S. population grew 7% between 2010 and 2020, according to census results. The age breakdown isn’t yet available, but a smaller sample by the Census Bureau and the Bureau of Labor Statistics shows that the working-age population — those 16 to 64 — grew just 3.3%. Because the share of those people working or looking for work has shrunk, the working-age labor force grew only 2%, and actually shrank last year. Some of those missing workers will return when the virus recedes. But many won’t: Baby boomer retirements have soared.
Reversing this move would require either a dramatic increase in births, which has eluded countries with more-family-friendly policies, or immigration, which is politically hard.
The demographic squeeze is far more severe in China, which admits almost no immigrants and for years limited families to one child. Tuesday, authorities said the population in China had grown just 5.4% in the past decade. The working-age population — those 15 to 59 — shrank 5%, or roughly 45 million people. When worker shortages began emerging over a decade ago, factories began moving to poorer inland provinces and then cheaper countries including Vietnam. In recent years some indicators suggest jobs are getting harder to fill, though the data might not be nationally representative.
Author(s): Greg Ip
Publication Date: 12 May 2021
Publication Site: Wall Street Journal
Excerpt:
“Labor force participation—defined as all civilians working full or part time, as well as those who are unemployed but looking for work—fell dramatically for both genders between March and April 2020,” noted Gallup. In April 2020, men’s labor force participation was at 97.8 percent of its February 2020 level and women’s labor force participation was 96.9 percent of its February 2020 level—a gender gap of just 0.9* percentage points.By February 2021, labor force participation for both sexes had ticked back up somewhat. And while women were still seeing a less full recovery, the gap was again less than one percentage point. Compared to February 2020, men’s February 2021 labor force participation was 2.2 percent smaller and women’s was 3.1 percent smaller.
That’s not nothing—“the gap in labor force changes amounts to roughly 493,000 more women than men being absent from the labor force since the pandemic began,” Gallup pointed out in early March. But it’s also not evidence that women have been uniquely devastated by pandemic-related job losses, especially when—contra previous economic downturns—many of the circumstances that initially created the job losses will remedy quickly as life returns to a more normal pace.
Author(s): Elizabeth Nolan Brown
Publication Date: 11 May 2021
Publication Site: Reason