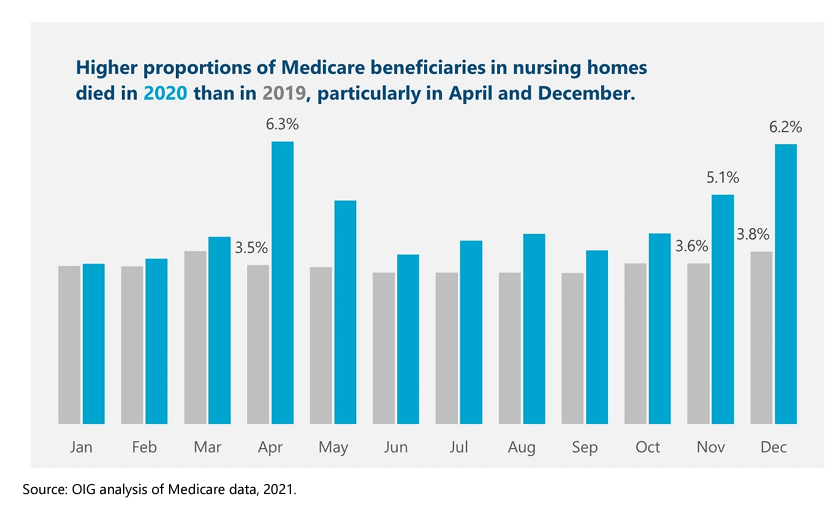
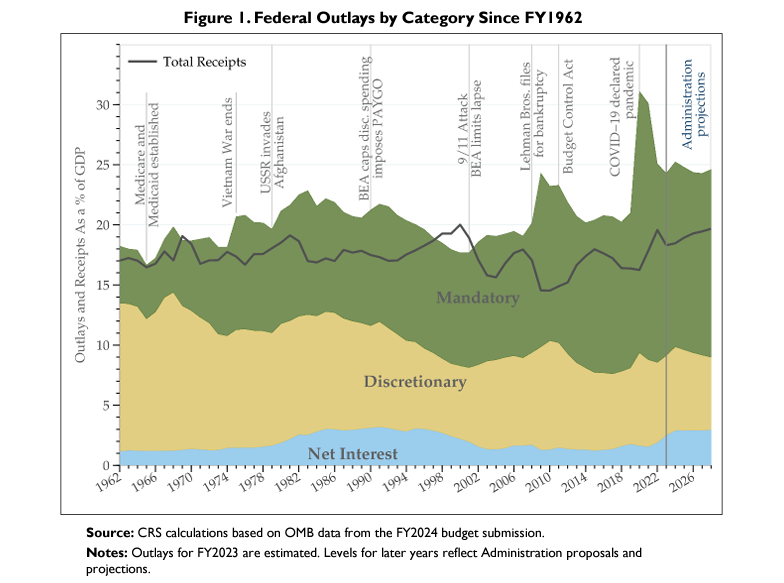
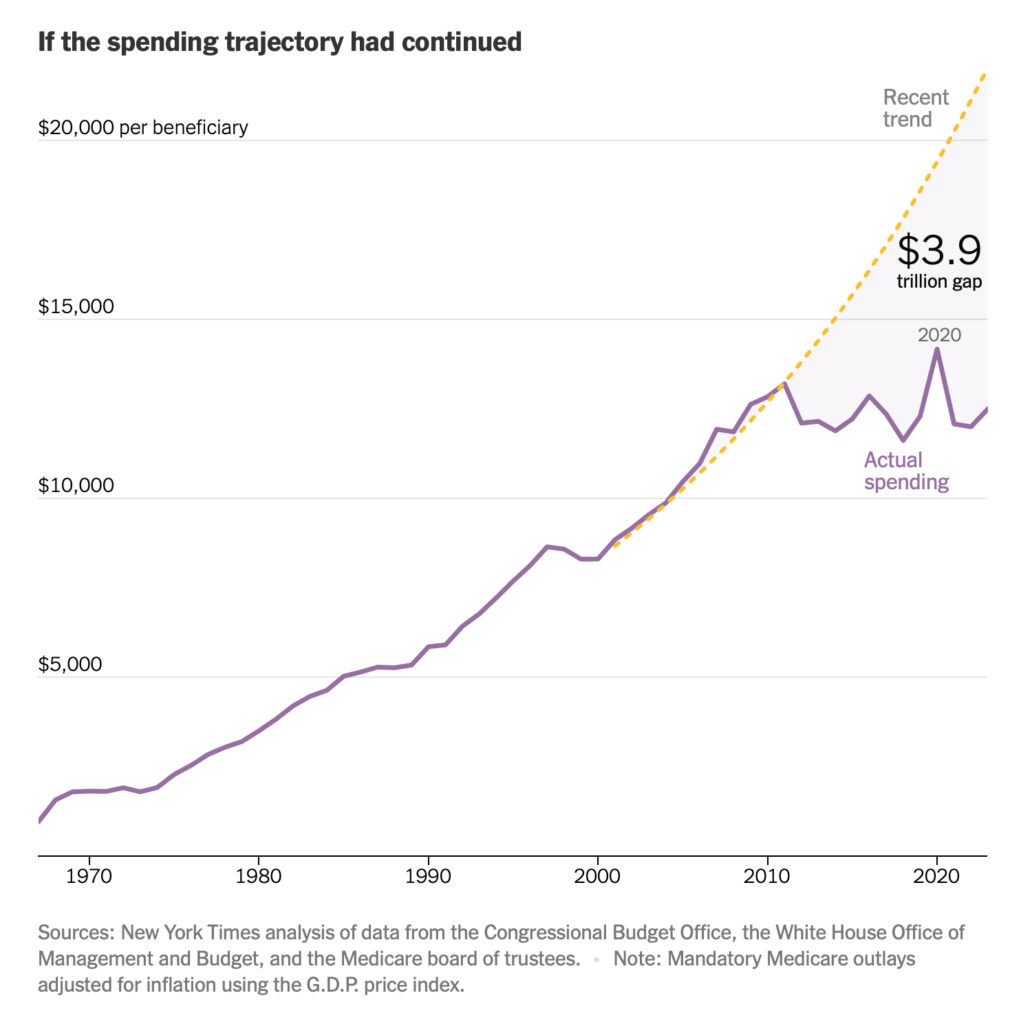
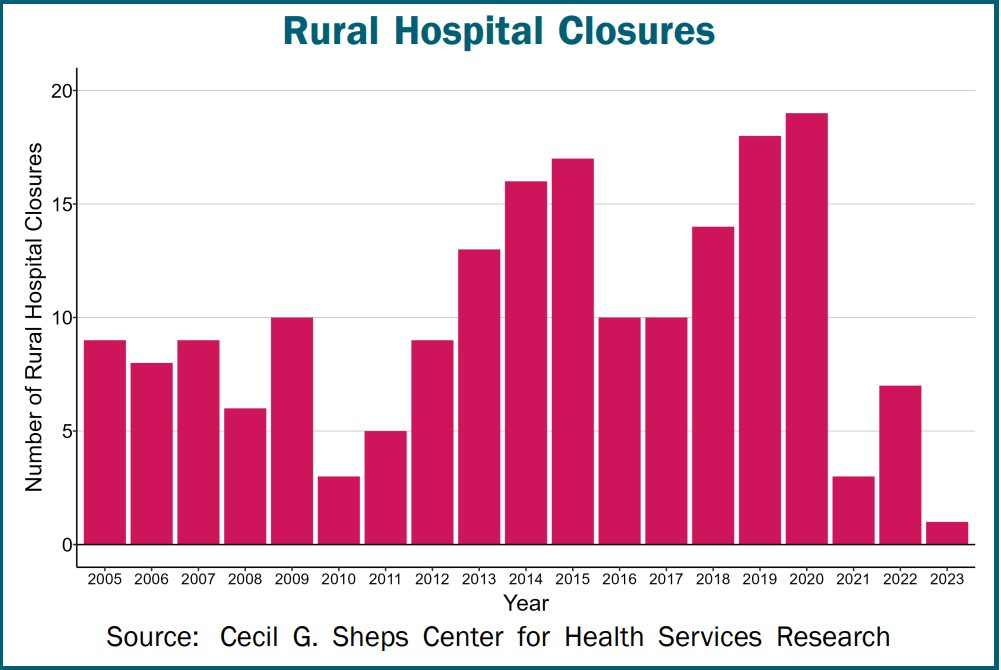
Graphic:
Excerpt:
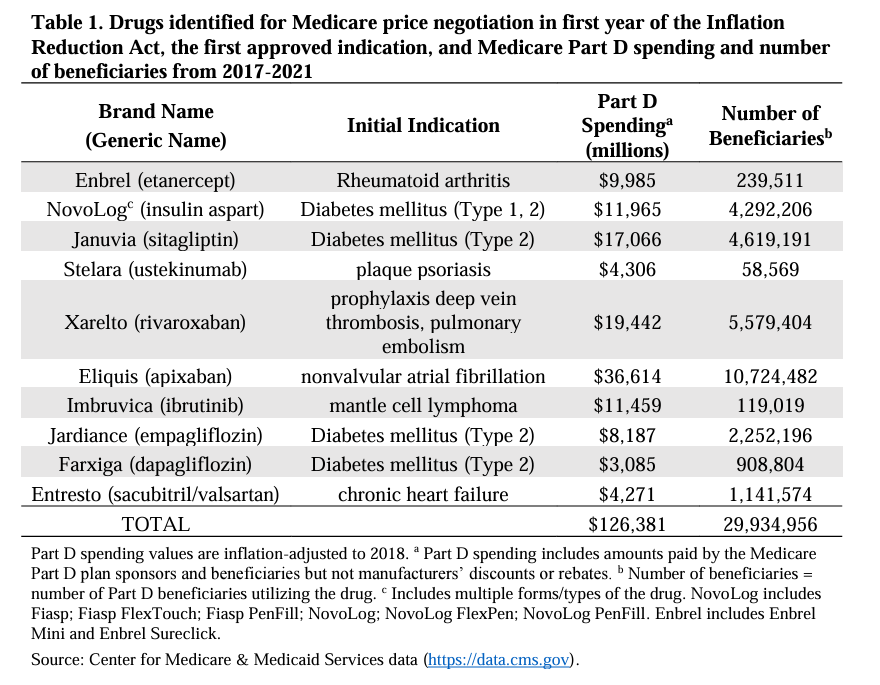
Now, at last, thanks to the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), the federal government will be allowed to negotiate a “maximum fair price” for drugs covered by Medicare Part D. This historical change, taking place in the face of intense industry opposition, incrementally reverses policies that have prohibited the government from engaging in price negotiations since Medicare Part D was first established in 2003. While only ten drugs will be subject to negotiation in the first year of the IRA and 90 over the first five years, negotiations are now ongoing.
….
It has been suggested that the government should negotiate for value-based pricing that would benchmark the Medicare Part D price measures of the health benefit provided to those using these drugs. This would be analogous to the approach currently used by most European countries for drug pricing. We believe this approach is inadequate and fails to provide the public with a return on the massive US government investments in biomedical research related to these drugs that enabled these products to be developed and commercialized in the first place.
….
In our new INET working paper, we extend these analyses to the ten drugs selected for Medicare price negotiation in the first year of the IRA. Our analysis reveals that the NIH spent $11.7 billion on basic or applied research related to the drugs selected for Medicare price negotiations, representing a median investment cost of $895.4 million per drug and, by making this research available to industry, saving industry a median of $1,485 million per drug. While data on industry investments in these ten drugs is not publicly available, this level of NIH investment is comparable to reported investment by industry in the drugs approved from 2010 to 2019.
Paper PDF: https://www.ineteconomics.org/uploads/papers/WP_219-Federal-spending-on-drugs-Ledley-et-al-final.pdf
Author(s): Fred Ledley
Publication Date: 4 Mar 2024
Publication Site: Institute for New Economic Thinking