Graphic:
Excerpt:
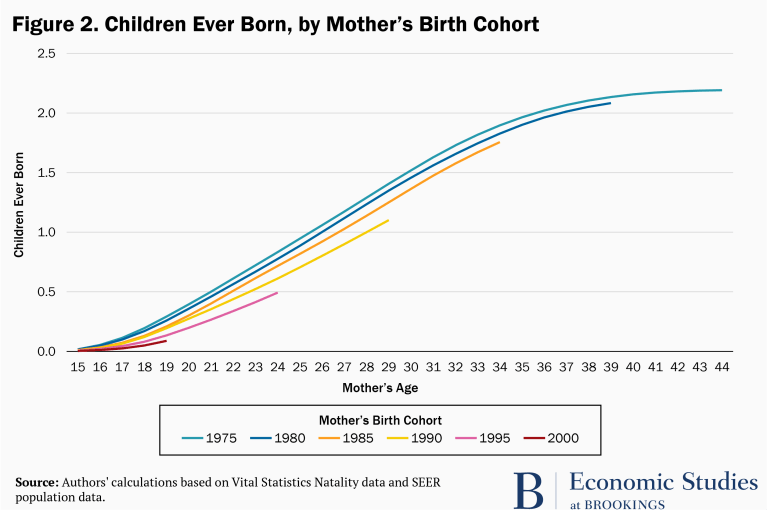
Figure 2 translates these childbearing age profiles into total number of children ever born by a certain age. The figure clearly shows that successively younger cohorts of women are having fewer children by specific ages. For instance, by age 24, the 1995 birth cohort of women had 38 percent fewer children than the 1975 and 1980 birth cohorts had at that age (0.5 compared to 0.8). This younger cohort would need to have 21 percent more children at each age from 25 through 44 to “catch up” to the earlier cohorts in terms of total lifetime childbearing. As another example, the 1990 birth cohort has had 21 percent fewer births through age 29 compared to the 1975 and 1980 cohorts; they would need to have 38 percent more births in their remaining childbearing years to catch up in terms of lifetime fertility.
Author(s): Melissa S. Kearney, Phillip Levine
Publication Date: 24 May 2021
Publication Site: Brookings