Link: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr72/nvsr72-07.pdf
Graphic:
Excerpt:
Objective—This report describes deaths from drug overdoses in 2020 in U.S. residents in 46 states and New York City by usual occupation and industry. August 22, 2023
Conclusions—Variation in drug overdose death rates and PMRs by usual occupation and industry in 2020 demonstrates the disproportionate burden of the ongoing drug overdose crisis on certain sectors of the U.S. workforce.
Methods—Frequencies, death rates, and proportionate mortality ratios (PMRs) are presented using the 2020 National Vital Statistics System mortality data file. Data were restricted to decedents aged 16–64 for rates and 15–64 for PMRs with usual occupations and industries in the paid civilian workforce. Age-standardized drug overdose death rates were estimated for usual occupation and industry groups overall, and age-adjusted drug overdose PMRs were estimated for each usual occupation and industry group overall and by sex, race and Hispanic-origin group, type of drug, and drug overdose intent. Age-adjusted drug overdose PMRs were also estimated for individual occupations and industries.
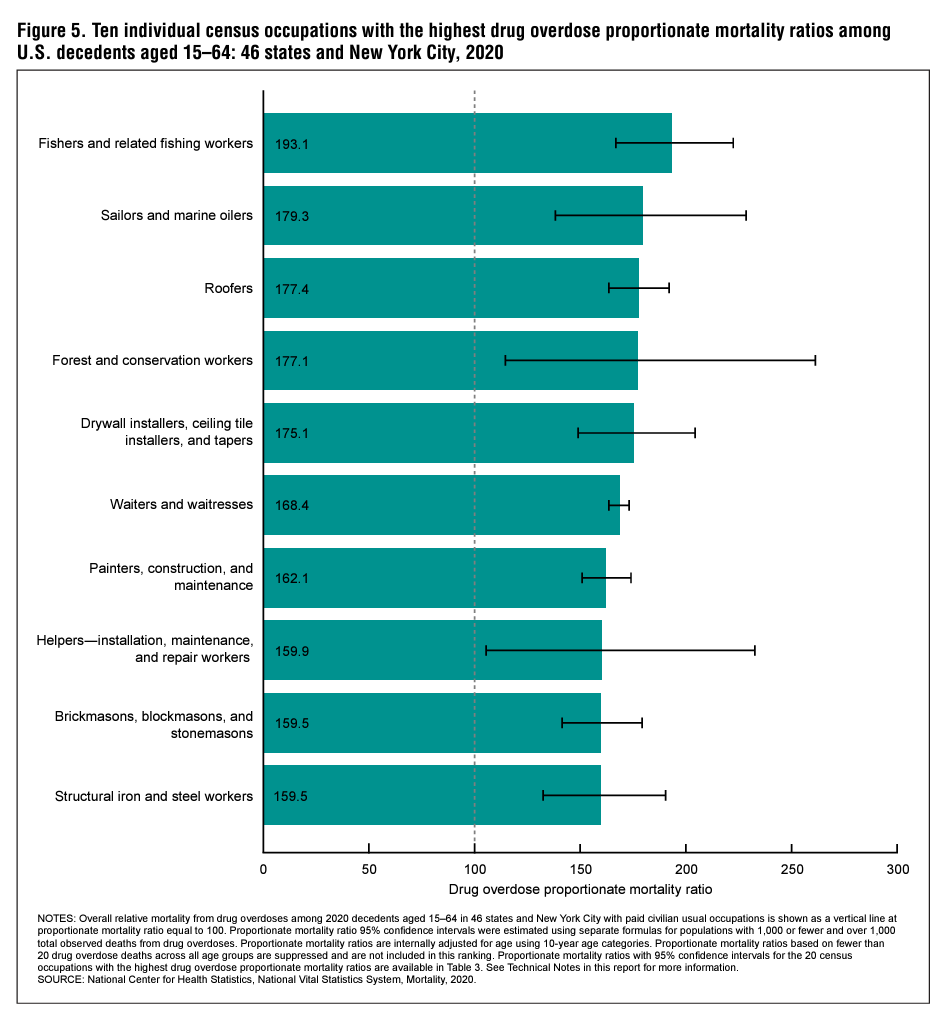
Results—Drug overdose mortality varied by usual occupation and industry. Workers in the construction and extraction occupation group (162.6 deaths per 100,000 workers, 95% confidence interval: 155.8–169.4) and construction industry group (130.9, 126.0–135.8) had the highest drug overdose death rates. The highest group-level drug overdose PMRs were observed in decedents in the construction and extraction occupation group and the construction industry group (145.4, 143.6–147.1 and 144.9, 143.2–146.5, respectively). Differences in drug overdose PMRs by usual occupation and industry group were observed within each sex, within each race and Hispanicorigin group, by drug type, and by drug overdose intent. Among individual occupations and industries, the highest drug overdose PMRs were observed in decedents who worked as fishers and related fishing occupations and in fishing, hunting, and trapping industries (193.1, 166.8–222.4 and 186.5, 161.7–214.1, respectively).
Author(s): Billock RM, Steege AL, Miniño A.
Publication Date: August 22, 2023
Publication Site: CDC, National Vital Statistics System