Link: https://www.nytimes.com/2023/10/03/opinion/life-expectancy-college-degree.html
Excerpt:
In the 1970s, American life expectancy grew by about four months each year. By the 1980s, it was similar to life expectancy in other rich countries. Since then, other countries have continued to progress, with life spans increasing by more than two and a half months a year.
But the United States has slowly, gradually and then precipitously fallen behind.
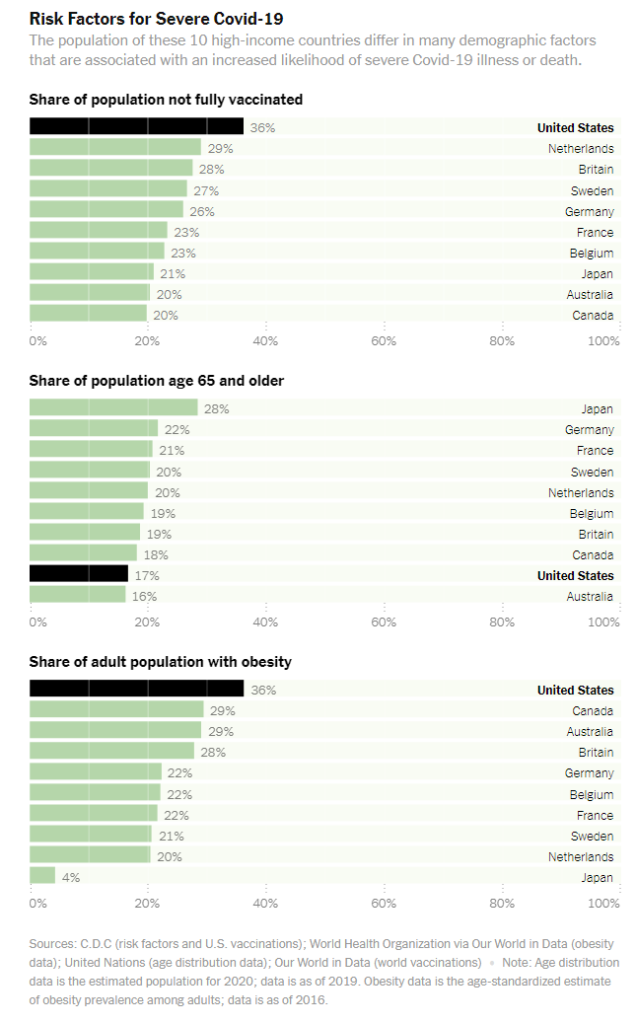
These ever-widening gaps have long troubled demographers and prompted three reports from the National Academy of Sciences. The gaps grew wider during the pandemic.
But even before, not only was life expectancy in the United States far from that of the best-performing countries (Japan and Switzerland), but it was also more than two years lower than that of the worst performers (Germany and Britain) among 22 other rich countries.
Public health authorities in the United States record educational qualifications at death so that, after 1992, we can calculate life expectancy by college degree, starting at age 25, when most people have completed their education. In new research using these individual death records, we have found startling results.
Life expectancy at age 25 (adult life expectancy) for those with four-year college degrees rose to 59 years on the eve of the pandemic — so an average individual would live to 84 — up from 54 years (or 79 years old) in 1992. During the pandemic, by 2021, the expectation slipped a year.
But we were staggered to discover that for those without college degrees, life expectancy reached its peak around 2010 and has been falling since, an unfolding disaster that has attracted little attention in the media or among elected officials.
Adult life expectancy for this group started out two and a half years lower, at 51.6, in 1992 — so an average individual would live to nearly 77 years old. But by 2021, it was 49.8 years (or almost 75 years old), roughly eight and a half years less than people with college degrees, and those without had lost 3.3 years during the pandemic.
The divergence of life expectancies on either side of the college divide — one going up, one going down — is both shocking and rare. We have found reference to only one other case in modern history, in the former Communist countries of Eastern Europe after the collapse of the Soviet Union. Like those countries, the United States is failing its less-educated people, an awful condemnation of where the country is today.
Author(s): Anne Case, Angus Deaton
Publication Date:
Publication Site: