Link: https://marypatcampbell.substack.com/p/mortality-with-meep-excess-mortality-8e2
Excerpt:
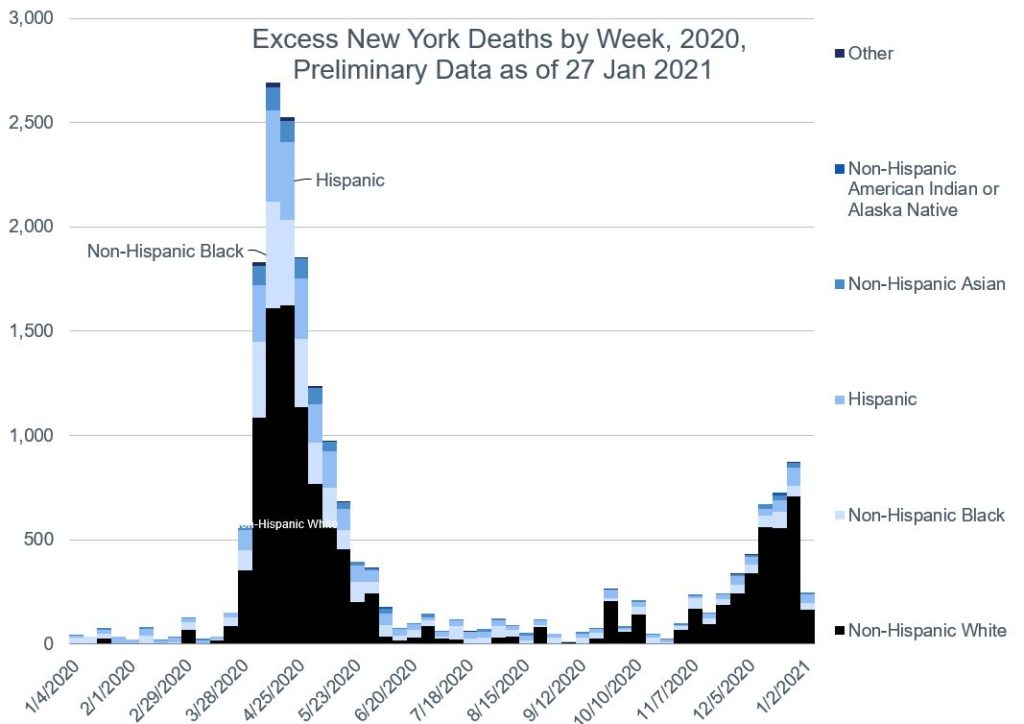
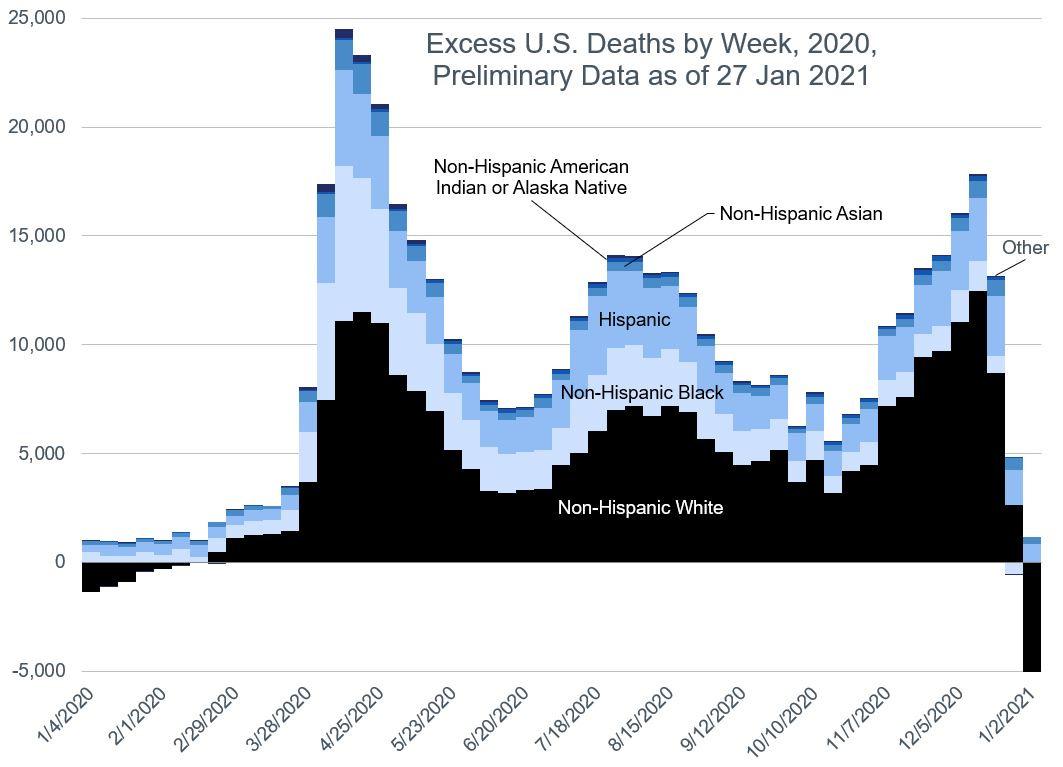
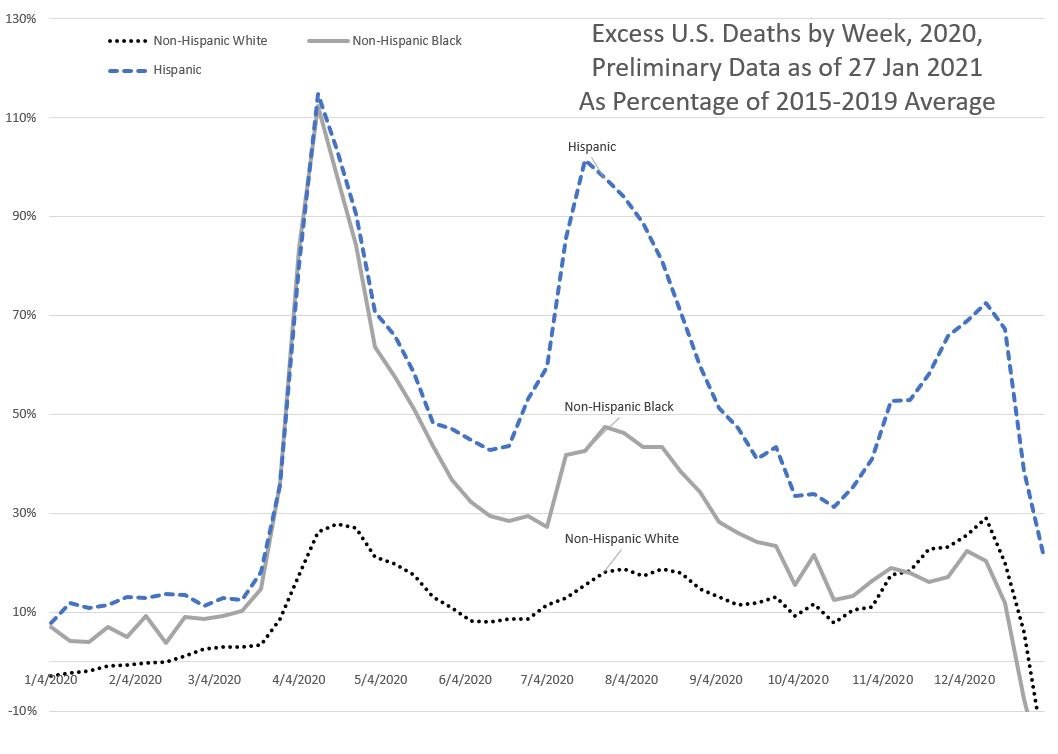
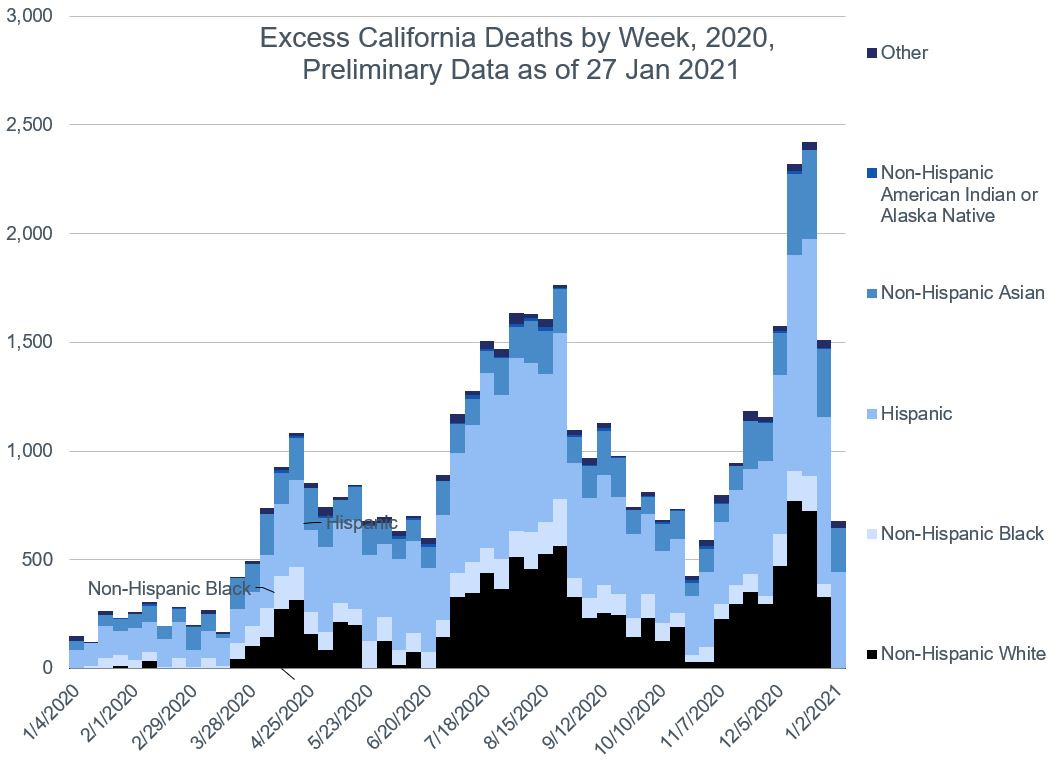
For Hispanics, it’s two thirds, with most of it coming from California (23%), then Texas (21%), then Florida (10%). New York City accounts for 9%, and then the rest of New York state for 3%.
UPDATE: Checking out the Hispanic population by state, these percentages are a little in line with national distribution — California (26% of U.S. Hispanic population), Texas (19%), Florida (9%), New York (including NYC — 6%). The most disproportionate effect comes from New York City.
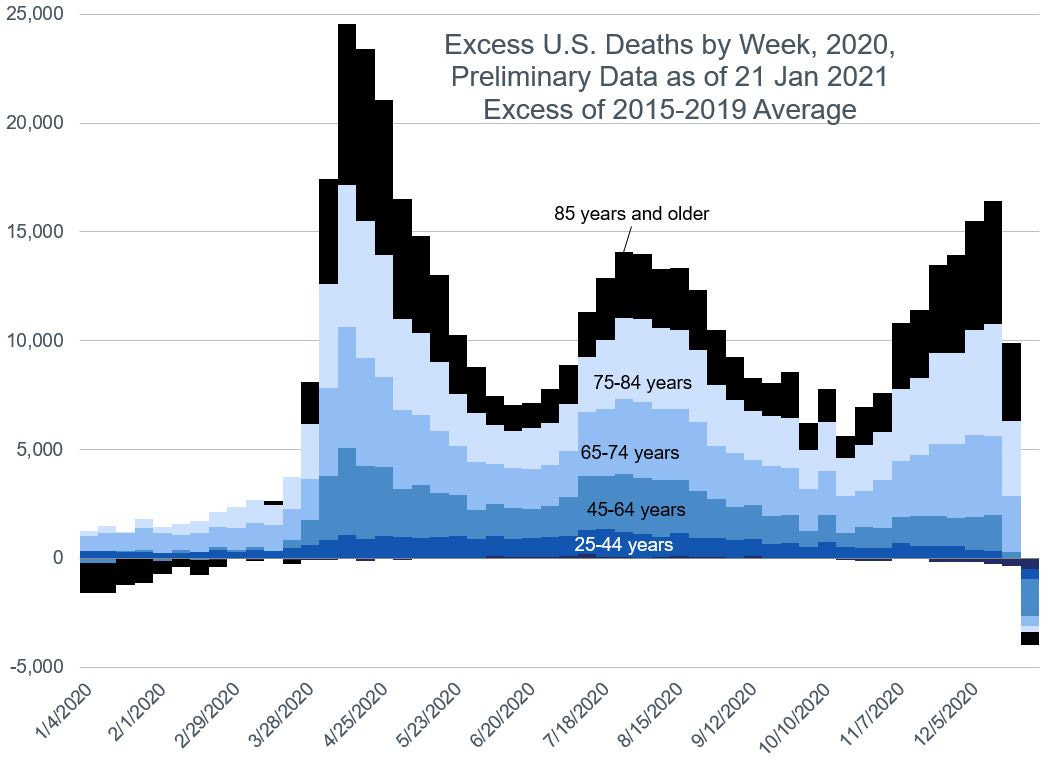
Graph:
Author: Mary Pat Campbell
Publication Date: 31 January 2021
Publication Site: STUMP