Excerpt:
The American Academy of Actuaries has released a new public policy paper and issue brief cautioning that clarification may be needed regarding estimated life expectancy showing significant decreases in light of the COVID-19 pandemic.
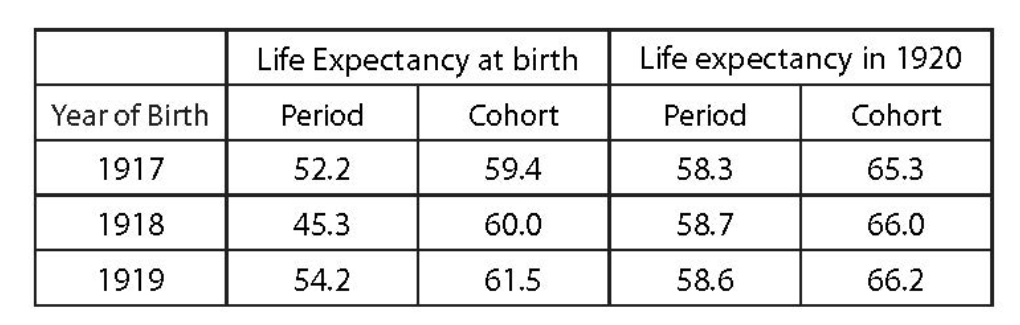
“Reports of considerable decreases in life expectancy driven by COVID-19 may certainly garner attention, but they can potentially be misleading when based on a technical measure that assumes heightened pandemic mortality will persist indefinitely,” said Academy Senior Pension Fellow Linda K. Stone. “Service to the public is core to the American Academy of Actuaries’ mission, and we would be remiss not to share the actuarial profession’s expertise to help the public interpret such reports.”
The Academy’s new Essential Elements paper, Clarifying Misunderstanding of Life Expectancy and COVID-19, which is based on a December 2021 issue brief developed by the Academy’s Pension Committee, Interpreting Pandemic-Related Decreases in Life Expectancy, cites the potential of confusion arising from recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates of significant life expectancy decreases primarily due to COVID-19. The CDC used a measurement known as “period life expectancy” to estimate life expectancy changes in 2020, publishing in July 2021 a preliminary estimate of a 1.5-year year-over-year decrease, and in December 2021 a final estimate of a 1.8-year decrease. However, the CDC’s methodology and the estimated decreases assume that the heightened mortality of the COVID-19 pandemic during the 2020 year will persist indefinitely—an unlikely scenario.
Author(s): American Academy of Actuaries
Publication Date: 14 Feb 2022
Publication Site: PRNEWSWIRE