Graphic:
Excerpt:
The purpose of this paper is to introduce the concept of capital and key related terms, as well as to compare and contrast four key regulatory capital regimes. Not only is each regime’s methodology explained with key terms defined and formulas provided, but illustrative applications of each approach are provided via an example with a baseline scenario. Comparison among these capital regimes is also provided using this same model with two alternative scenarios.
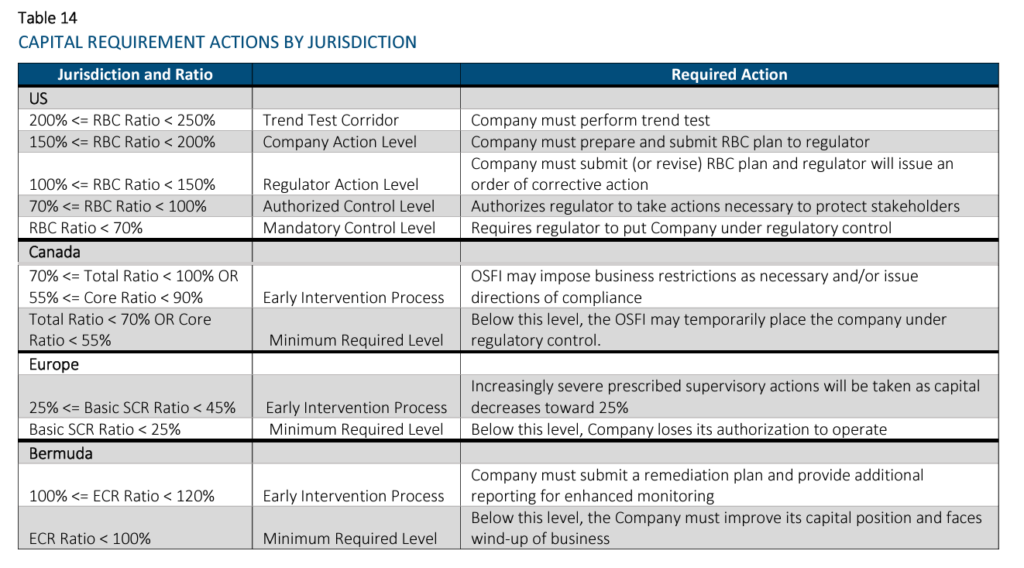
The four regulatory required capital approaches discussed in this paper are National Association of Insurance Commissioners’ (NAIC) Risk-Based Capital (RBC; the United States), Life Insurer Capital Adequacy Test (LICAT; Canada), Solvency II (European Union), and the Bermuda Insurance Solvency (BIS) Framework which describes the Bermuda Solvency Capital Requirement (BSCR). These terms may be used interchangeably. These standards apply to a large portion of the global life insurance market and were chosen to give the reader a better understanding of how required capital varies by jurisdiction, and the impact of the measurement method on life insurance company capital.
All of these approaches are similar in that they identify key risks for which capital should be held (e.g., asset default and market risks, insurance risks, etc.). However, they differ in significant ways too, including their defined risk taxonomy and risk diversification / aggregation methodologies, as well as required minimum capital thresholds and corresponding implications. Another key difference is that the US’s RBC methodology is largely factor-based, while the other methodologies are model-based approaches. For the model-based approaches, Solvency II and BIS allow for the use of internal models when certain conditions are satisfied. Another difference is that the RBC methodology is largely derived using book values, while the others use economic-based measurements.
As mentioned above, this paper provides a model that calculates the capital requirements for each jurisdiction. The model is used to compare regulatory solvency capital using identical portfolios for both assets and liabilities. For simplicity, we have assumed that all liabilities originated in the same jurisdiction as the calculation. As the objective of the model is to illustrate required capital calculation methodology differences, a number of modeling simplifications were employed and detailed later in the paper. The model considers two products – term insurance and payout annuities, approximately equally weighted in terms of reserves. The assets consist of two non-callable bonds of differing durations, mortgages, real estate, and equities. Two alternative scenarios have been considered, one where the company invests in riskier assets than assumed in the base case and one where the liability mix is more heavily weighted to annuities as compared to the base case.
Author(s): Ben Leiser, FSA, MAAA; Janine Bender, ASA, MAAA; Brian Kaul
Publication Date: July 2023
Publication Site: Society of Actuaries