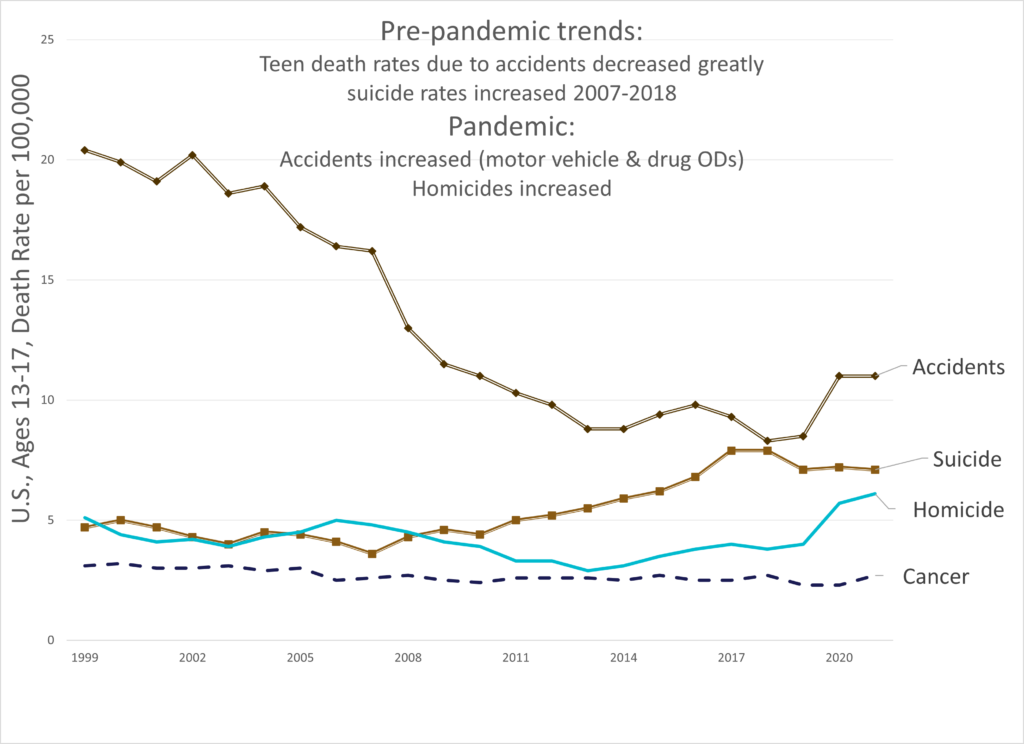
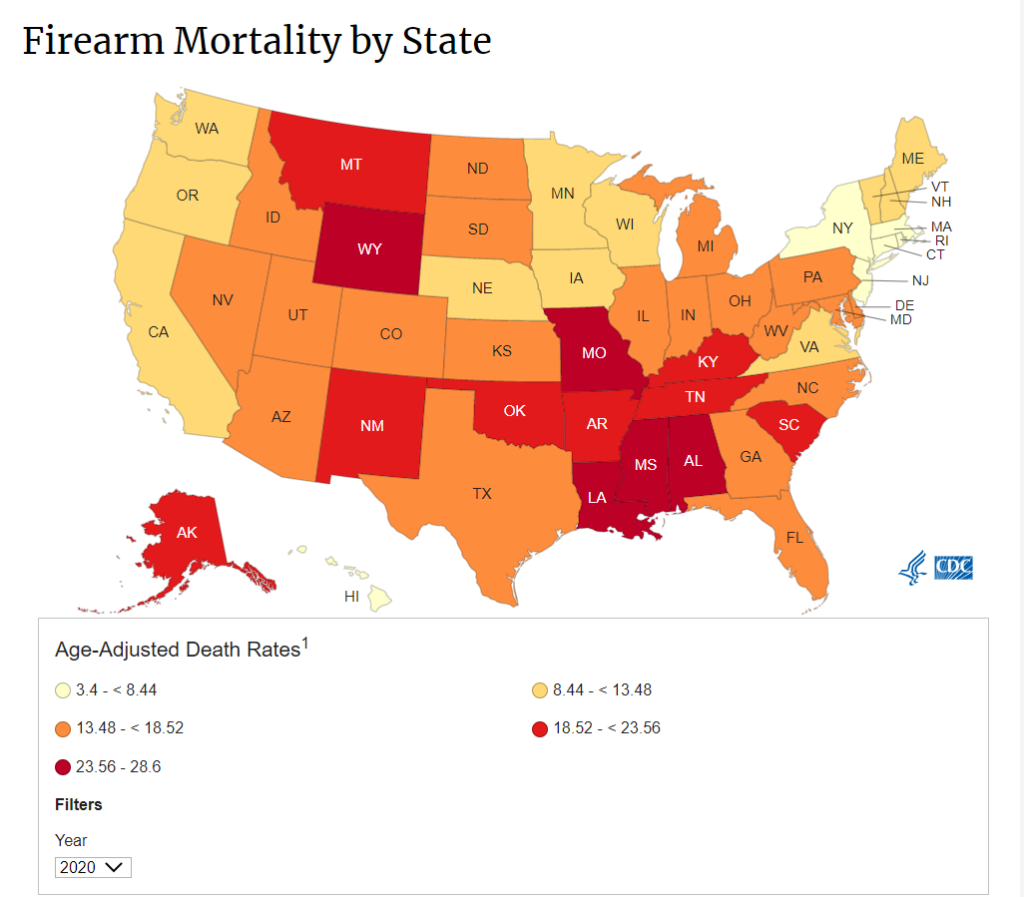
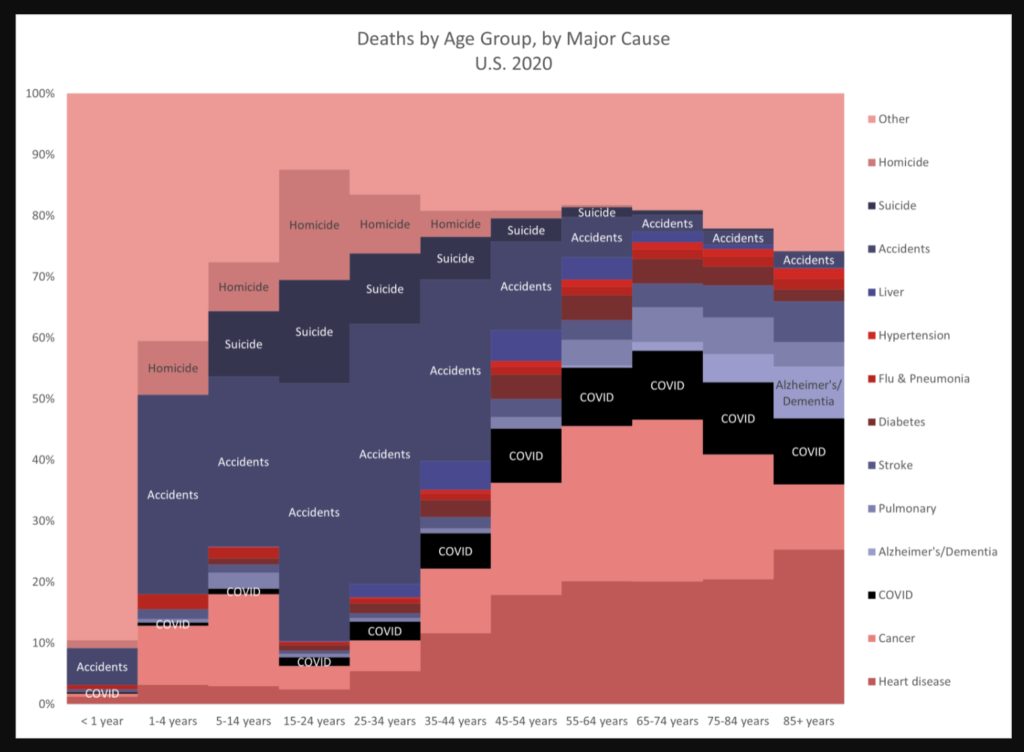
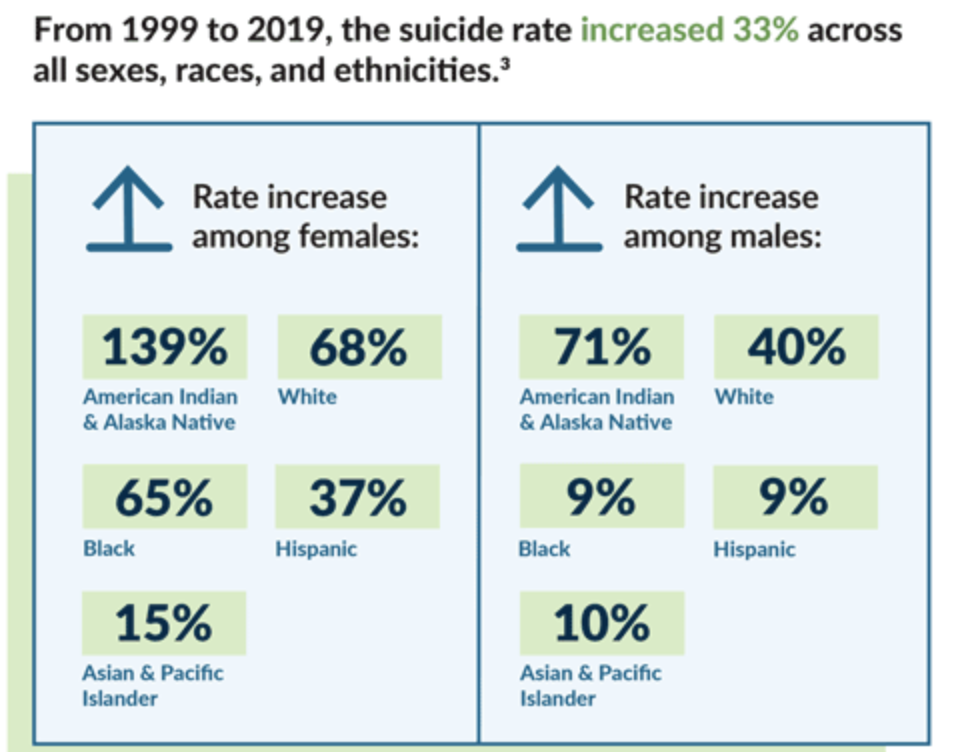
Graphic:
Excerpt:
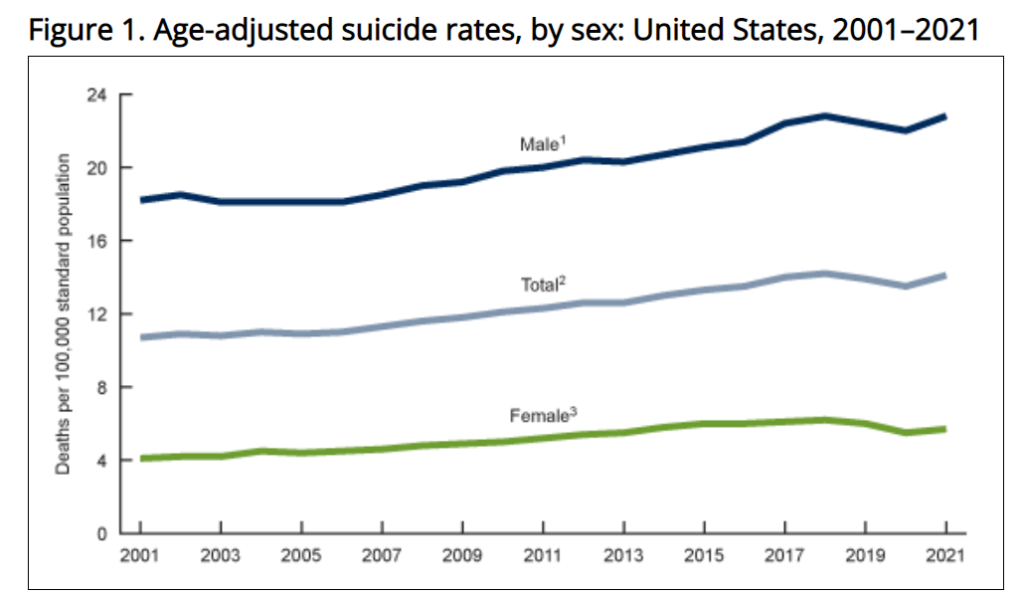
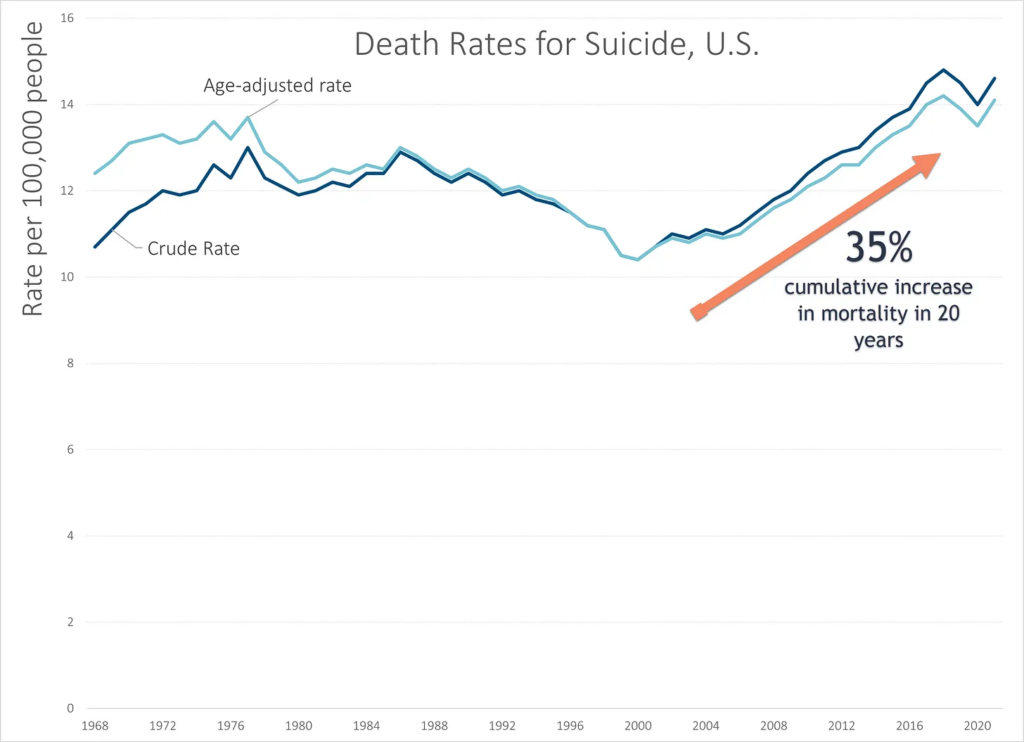
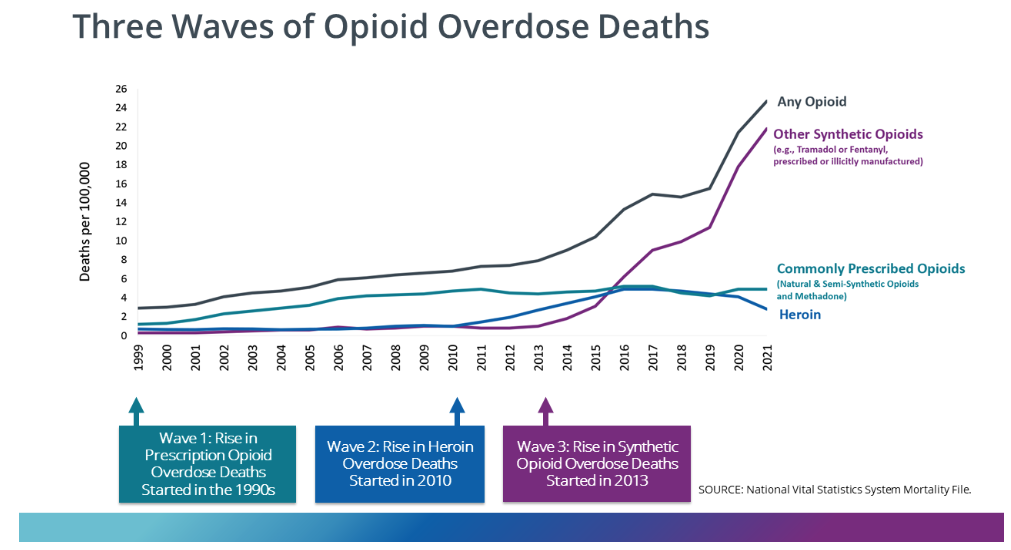
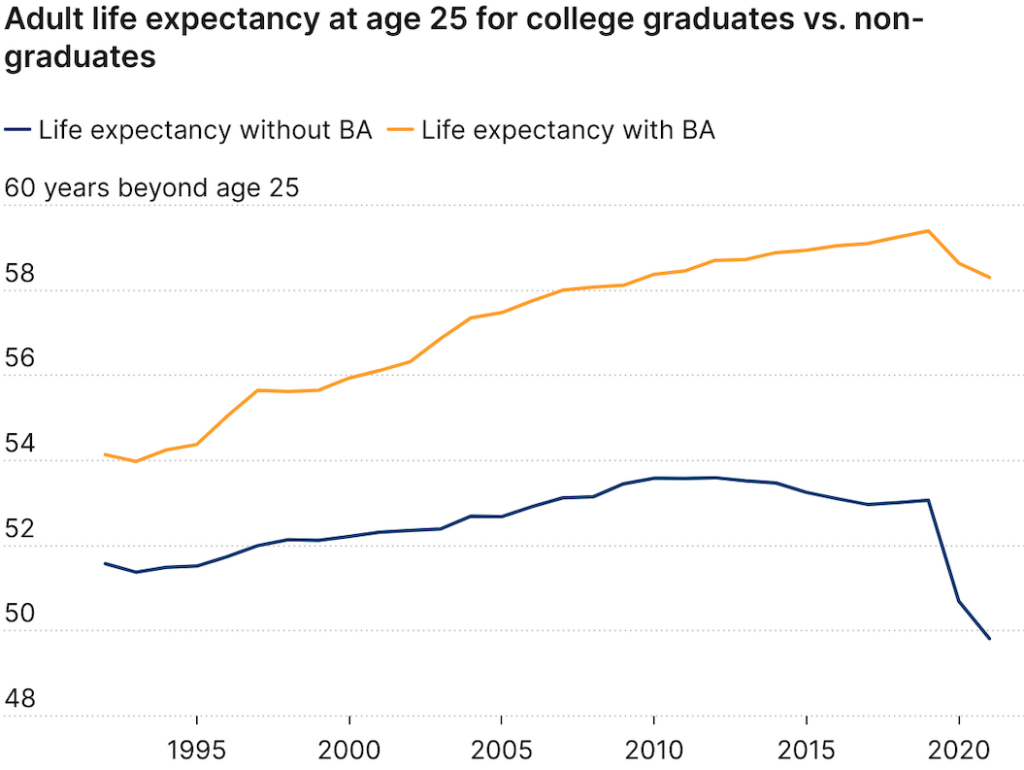
The Post reported that some politicians pointed to the rising death toll from “lethal drug overdoses” as a significant factor in declining U.S. life expectancy. The Post did, however, acknowledge that drug deaths “are not solely responsible for the decline in life expectancy.” It is worth noting that opioid overdose deaths began truly soaring after 2010 when users turned to illicit heroin and fentanyl after the introduction of Food and Drug Administration–approved abuse-deterrent formulations.
So how much do drug overdose deaths contribute to the recent decline in U.S. life expectancy? A 2021 comprehensive review of factors affecting mortality trends in the U.S. between 1999 and 2018 found that average life expectancy would “have been 0.3 years greater were it not for increases in unintentional drug poisoning.” In a 2023 preprint article, two Johns Hopkins University researchers calculated that opioid overdose deaths between 2019 and 2021 reduced U.S. life expectancy by 0.65 years. If politicians and policy makers really want to make increasing life expectancy a priority, one huge step would be to actually end the war on drugs. A cease-fire in the drug war would likely reduce gun deaths too.
Author(s): Ronald Bailey
Publication Date: 8 Jan 2024
Publication Site: Reason