Link: https://www.city-journal.org/covid-19-lockdowns-exposed-cities-deep-seated-financial-troubles
Graphic:
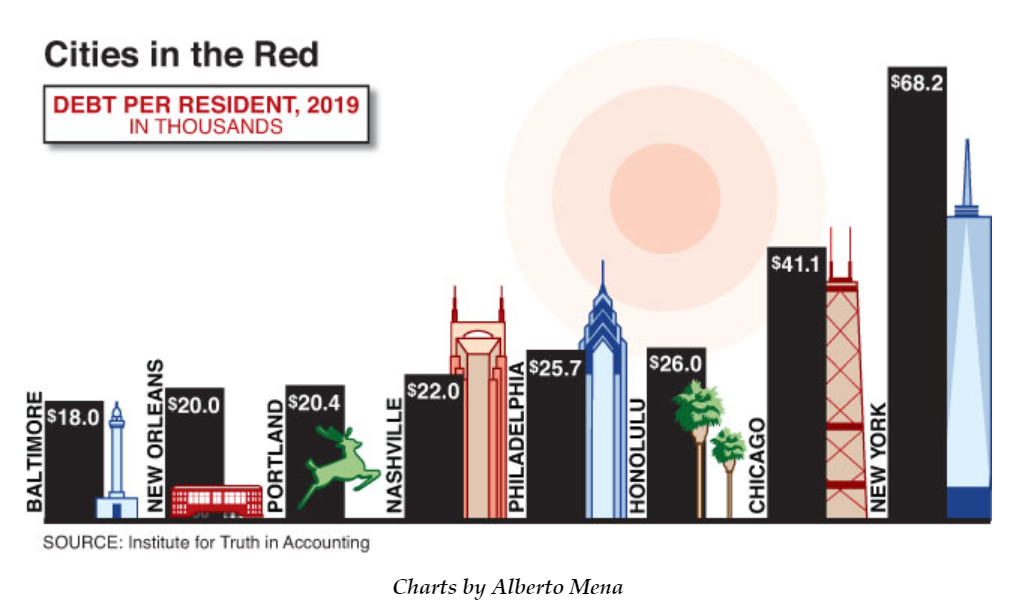
Excerpt:
The past year has been a fiscal nightmare for Nashville. Covid-19 helped punch a $332 million hole in the city’s $2.46 billion budget. Tennessee state comptroller Justin Wilson warned that, without drastic action, the state might take over management of Nashville’s affairs. In response, the city council raised property taxes 34 percent, spurring a citizen revolt in the form of a ballot initiative to overturn the tax hike. Without the extra revenue, however, Mayor John Cooper’s administration said that drastic cuts would be unavoidable: “Few corners of the Metro government, including emergency services and schools, would be spared significant reductions or eliminations.”
Nashville’s budget woes predate the pandemic: the city began borrowing money to cover deficits after the Great Recession of 2008–09. City leaders, at the same time, went into heavy debt to build new government-owned attractions, offered workers health retirement benefits that they haven’t funded, and deep-sixed pension reforms that saved the state billions of dollars. In fact, back in December 2019, the state comptroller issued a similar warning to Nashville about its shaky finances.
The Music City isn’t alone. The Covid health emergency and accompanying economic downturn caused budget crises for municipalities—cities, counties, and school districts—across America. A February letter from 400 mayors to President Biden said that the pandemic-inflicted strain on municipal budgets had “resulted in budget cuts, service reductions, and job losses” throughout local government. America’s largest city, New York, grappled with a nearly $10 billion budget deficit in the spring of 2020, while Chicago struggled with a $2 billion gap. Dozens of local governments used the crisis to justify budget maneuvers that fiscal experts generally frown upon, from borrowing money to close deficits to issuing bonds to fund employee pensions.
Author(s): Steven Malanga
Publication Date: Summer 2021
Publication Site: City Journal