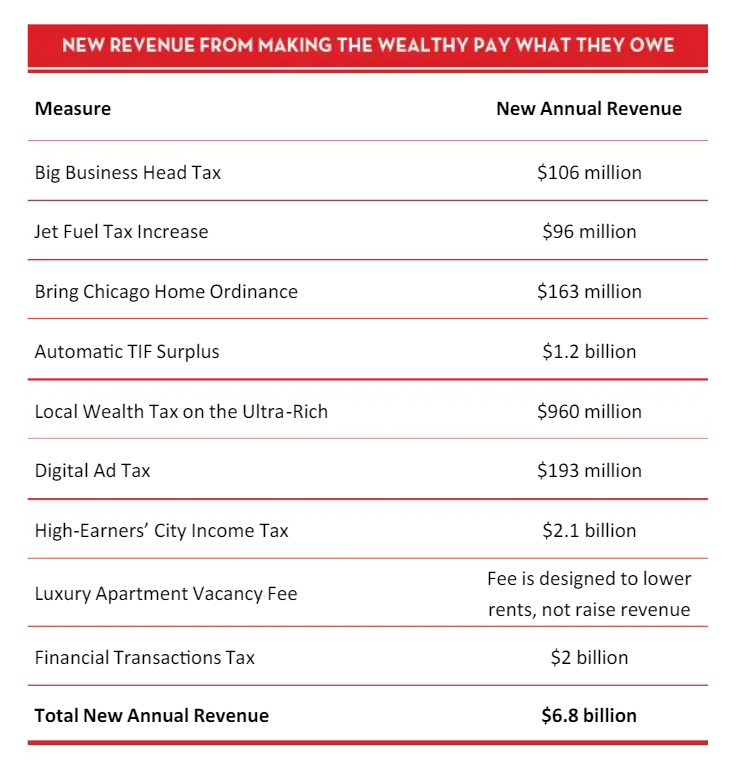
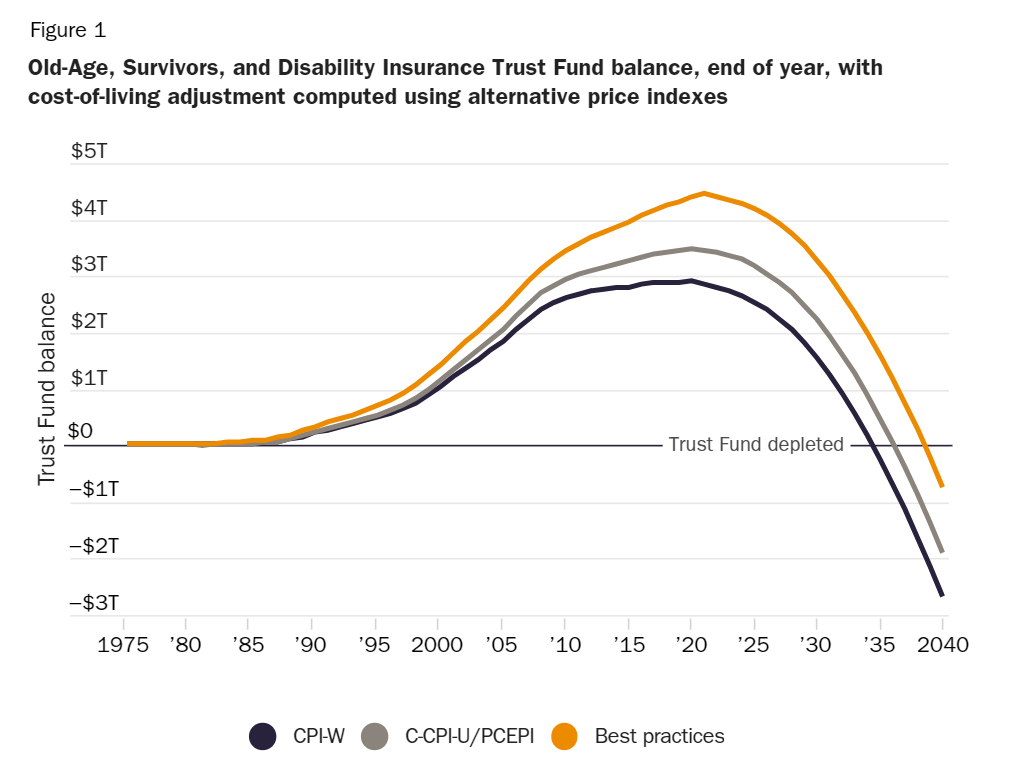
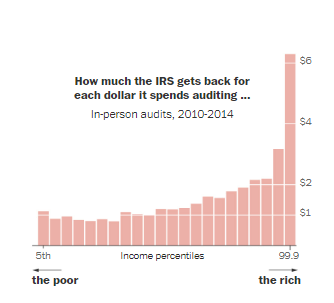
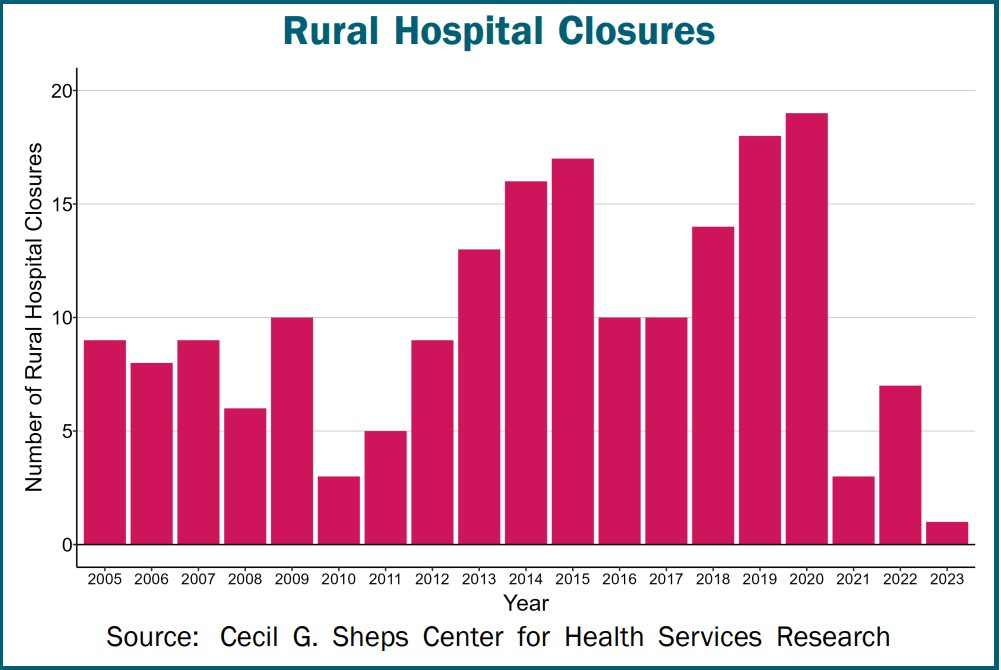
Graphic:
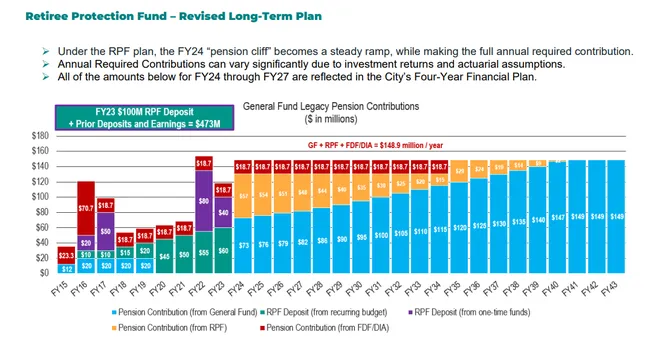
Excerpt:
The Police and Fire Retirement System of Detroit filed on Monday a motion for reconsideration, pushing back on a federal bankruptcy judge’s ruling in favor of the Duggan administration’s plan to extend the city’s pension payment obligations over 30 years rather than 20 years.
The city’s police and fire retirees are continuing litigation that has been ongoing since August when the city administration initially filed suit against the pension system to enforce a 30-year pay-out schedule. On June 26, Judge Thomas Tucker ruled in the city’s favor, stating that a 30-year amortization period is “indeed part of the (bankruptcy) Plan of Adjustment and that the Police Fire Retirement System cannot change it.”
The new motion seeks clarification of the court’s possible imposition of a 6.75% rate of return that was specifically set to expire after 10 years under the Plan of Adjustment, the bankruptcy exit plan. After June 30, the pension fund’s rate of return and its amortization funding policy are within the purview of the Police and Fire Retirement System’s Board of Trustees and Investment Committee, according to the pensioners’ filing.
At the 30-year determined rate, the city will complete its debt obligations in 2054. Police and fire retirees want their pension fund to be made whole sooner.
Author(s): Sarah Rahal
Publication Date: 11 July 2023
Publication Site: The Detroit News