Graphic:
Excerpt:
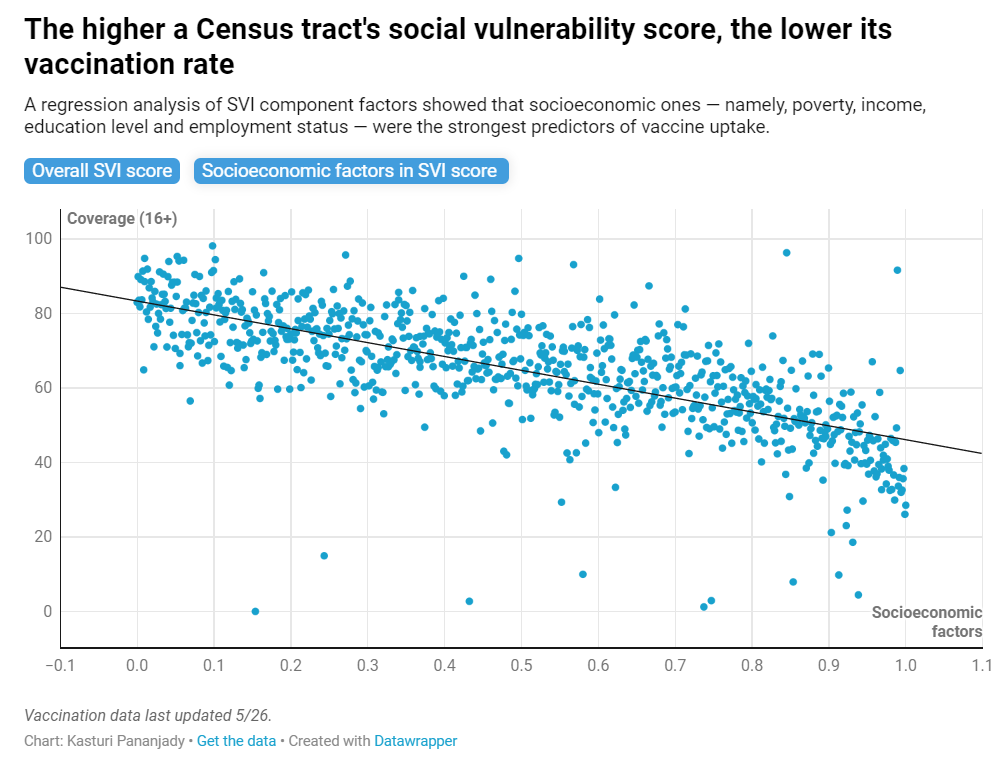
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s “social vulnerability index” has formed the basis for the state’s prioritization system and has been a reliable indicator of low vaccine uptake. Generally speaking, the higher a community’s SVI score, the lower its vaccination rate, a CT Mirror analysis found.
An estimated 32% of the state’s eligible population lives in the state’s priority ZIP codes, and the state aims to administer the same percentage of vaccines within those communities. While the state inches closer to that goal each week, the statewide slowdown in the number of shots administered means that it has a lot of ground to make up. Of all the vaccines administered so far, just 25% of all vaccines distributed as of last week have gone to residents of those ZIP codes.
“Progress is slower now,” said Josh Geballe, the state’s chief operating officer, at a recent press conference.
Of the 15 different variables that determine a Census tract’s vulnerability score, a CT Mirror analysis found that socioeconomic factors considered by the index — namely income, employment status, poverty level and education — were found to be most predictive of vaccination rates. This is consistent with a national study on the county level that the CDC released in March.
Author(s): KASTURI PANANJADY, DAVE ALTIMARI
Publication Date: 3 June 2021
Publication Site: CT Mirror